-
- HOME
- ABOUT US
- SOLUTION
- PROJECTS
- INDUSTRIES
- CLIENT NETWORK
- CAREER
- CONTACT WooCommerce not Found
- Newsletter
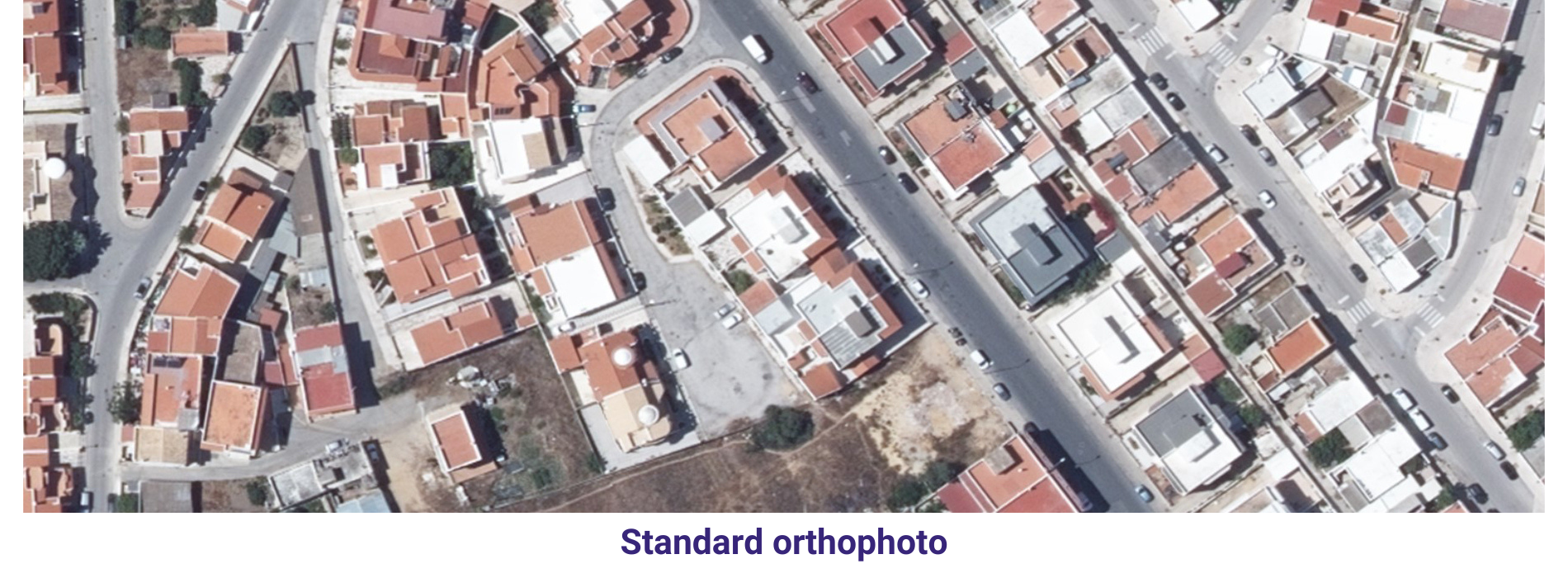
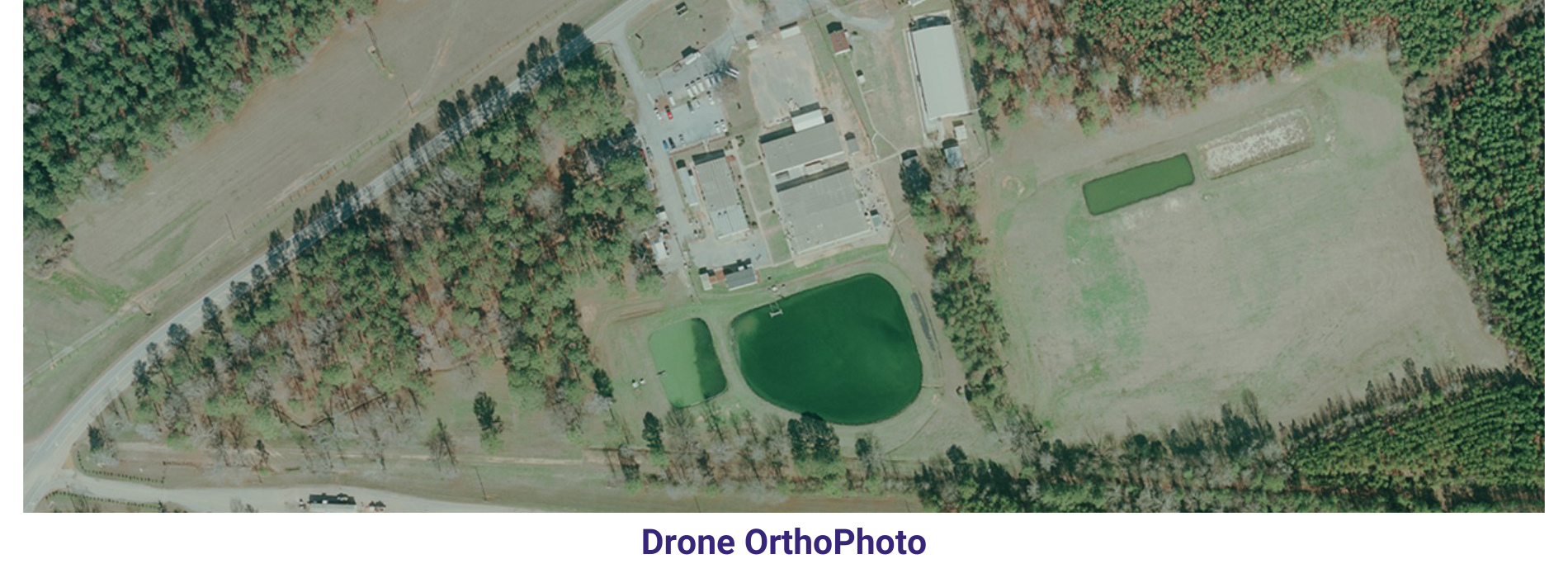
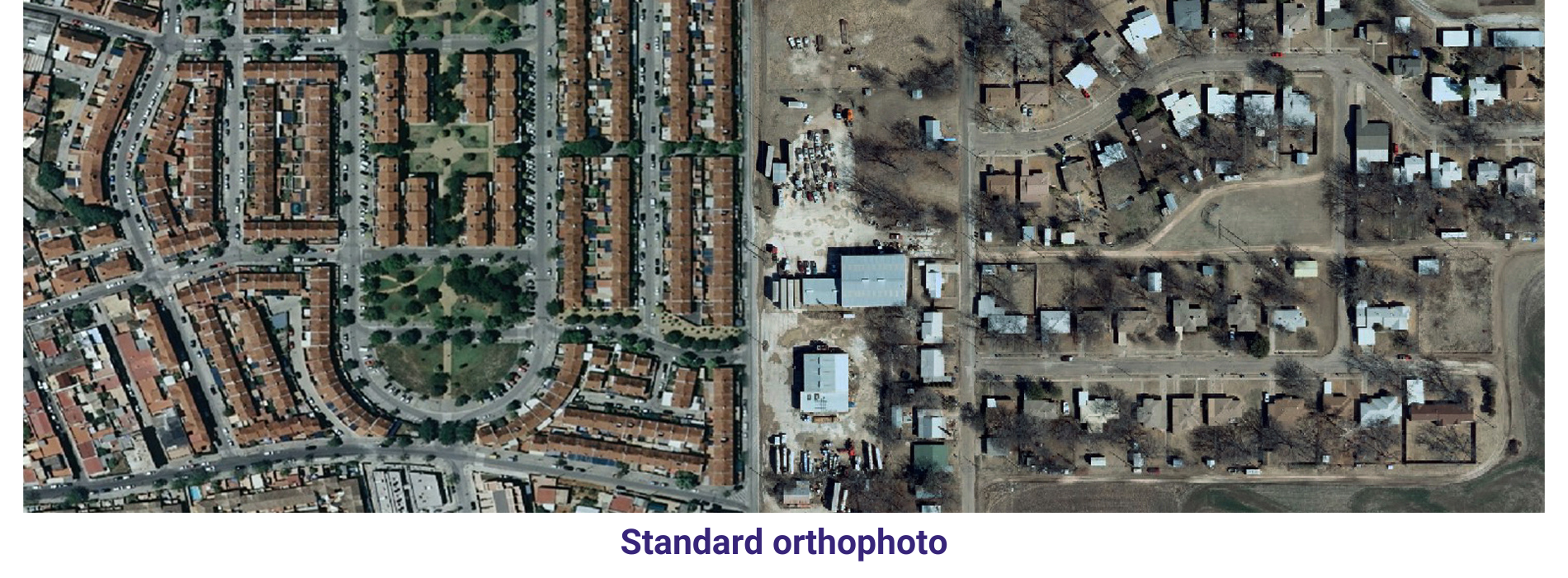
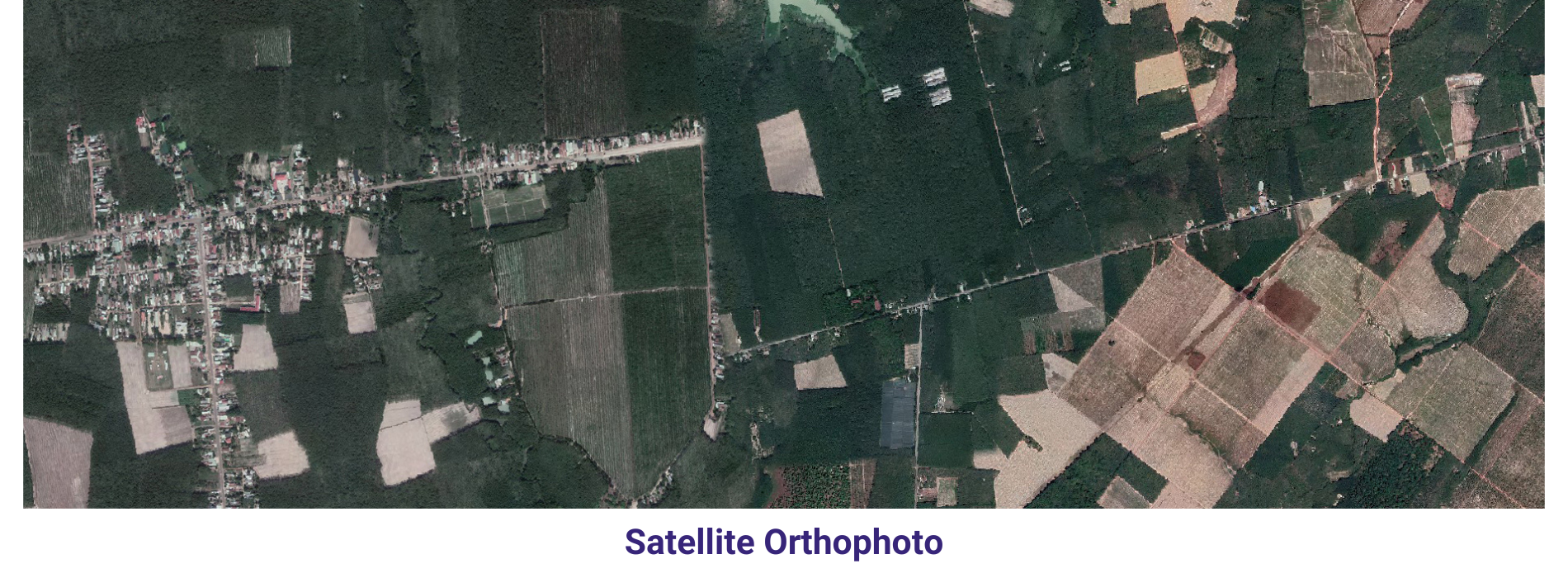
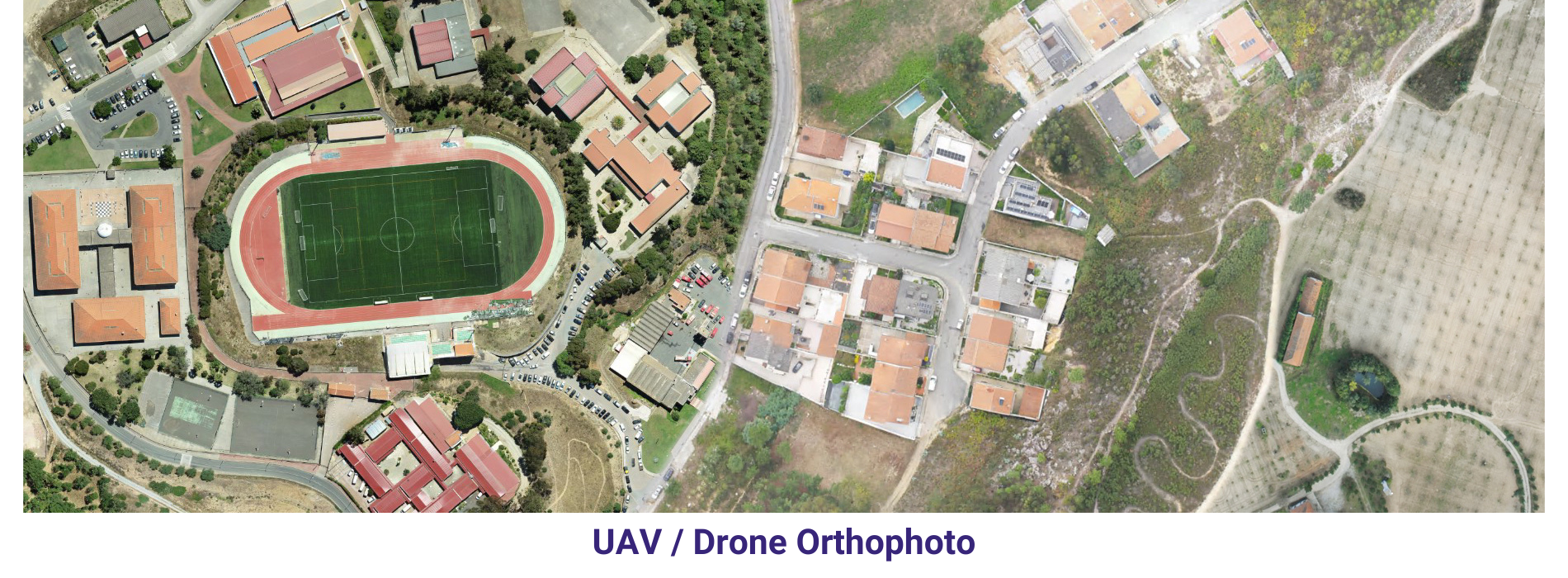
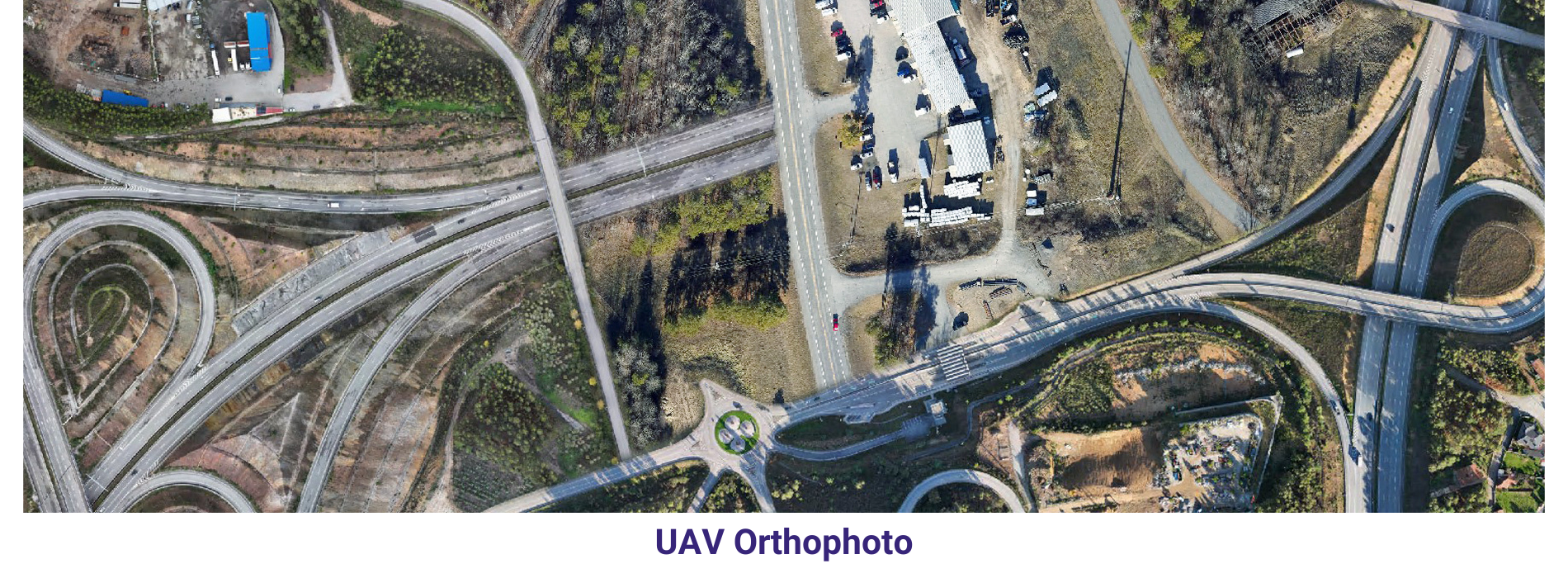
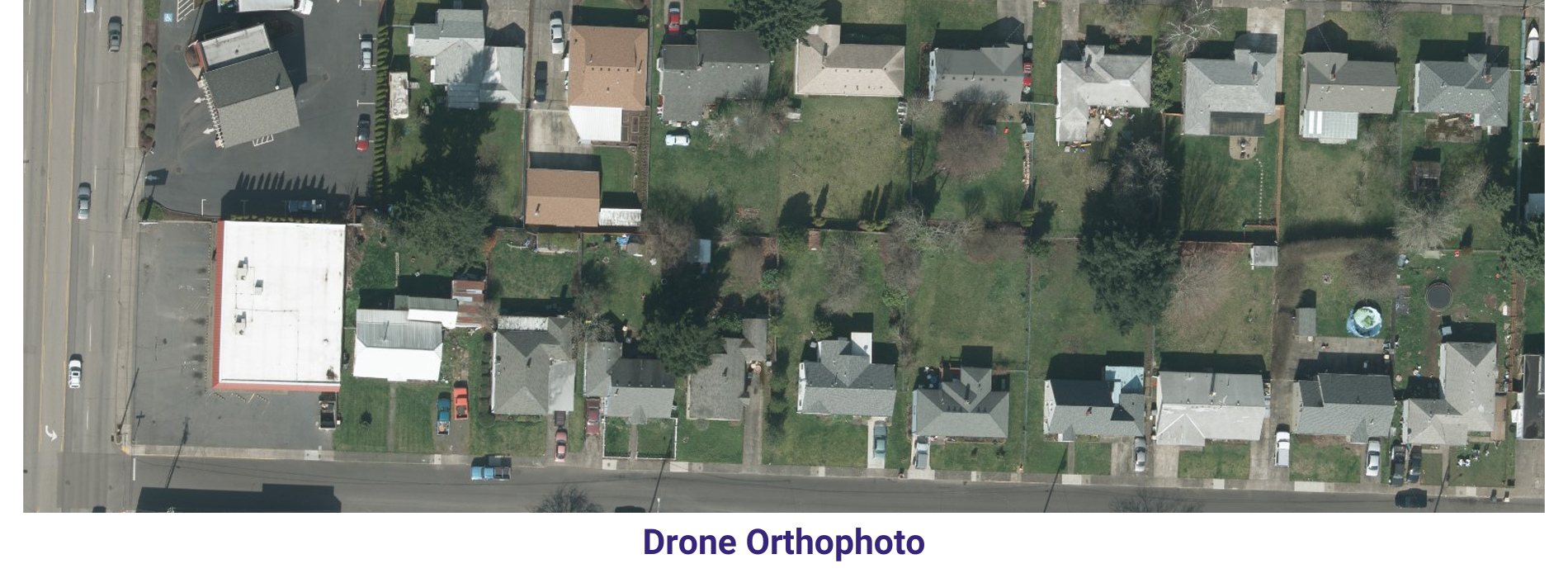
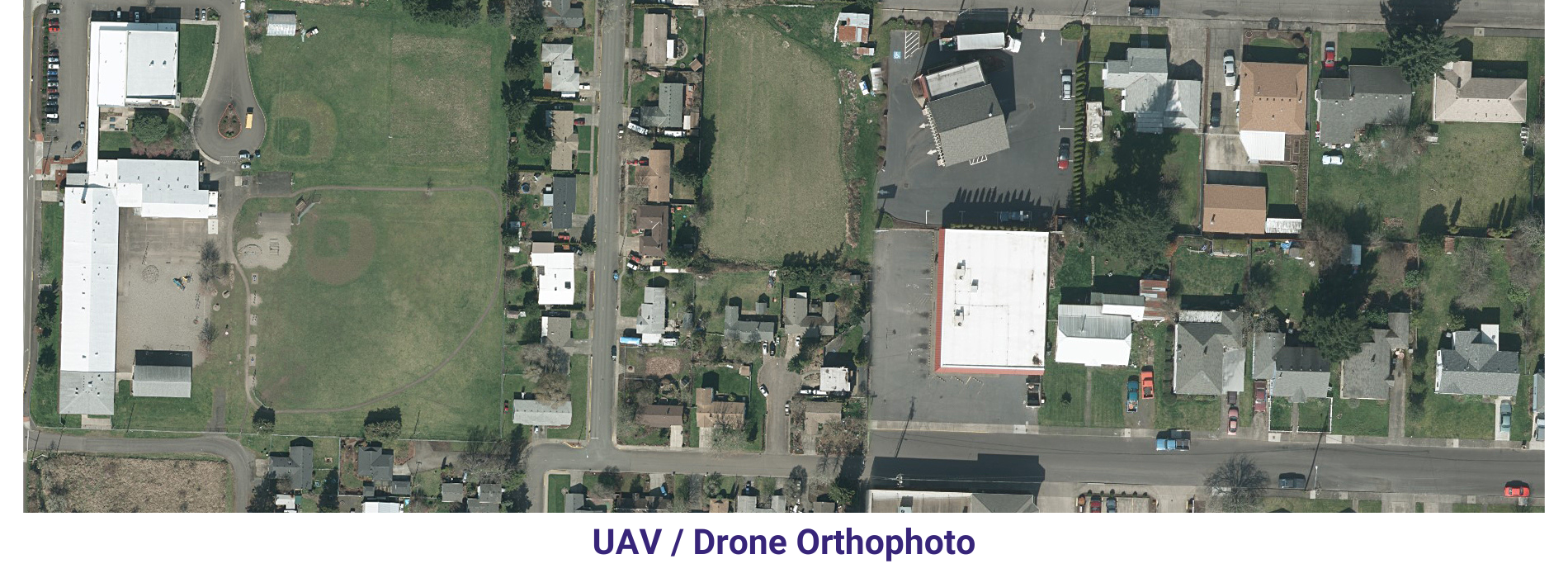




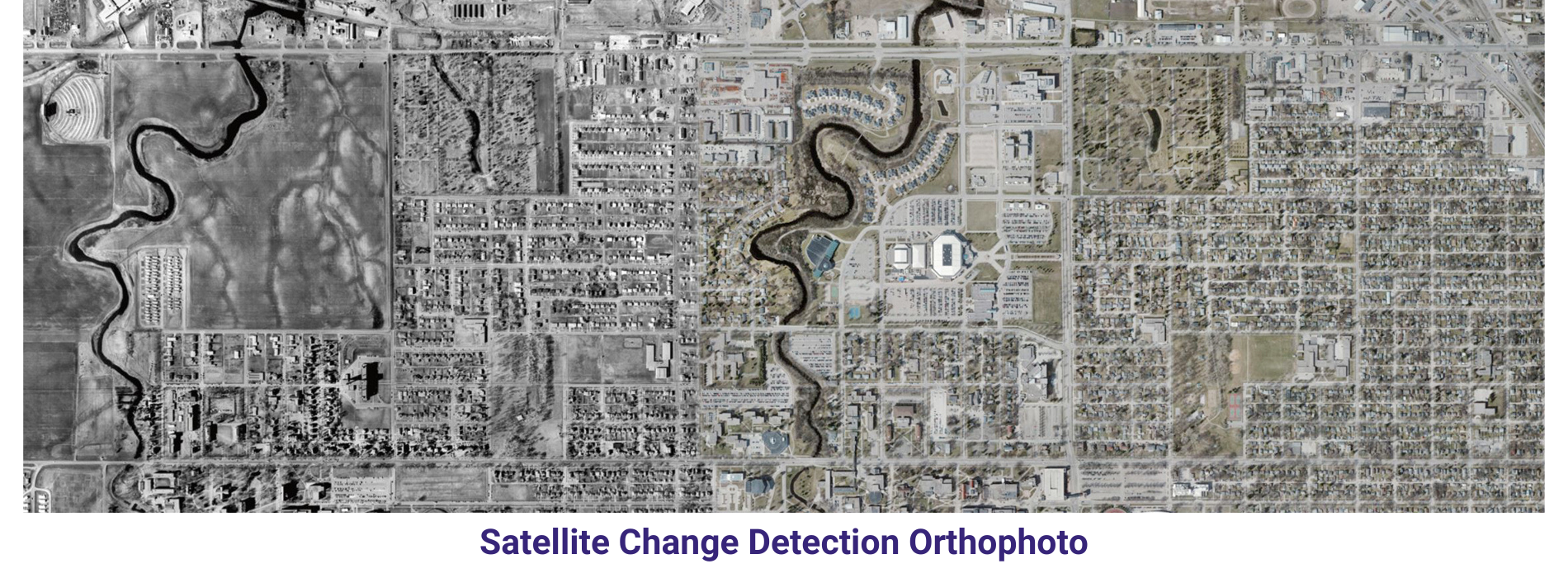













Orthophoto & Mosaicing In order to keep pace with ongoing competition, AAMGST is constantly innovating to find newer solutions, technologies and methodologies that can help our clients to ensure higher quality.
AAMGST has delivered orthophotos from aerial frames(300W) and 1.5 million Sqkm from satellite data. Orthophotos with high accuracy and radiornetically enhanced from different sensors (aerial frame, digital camera, ADS40 and satellite) with various GSDs (0.08, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5 and 1.0 meters).
By following all the standards of FGDC, we have generated orthophotos (from multiband images) by adopting the best practices in production and quality checking.
Final output has been delivered as per clients required projections and formats.
Orthophoto and mosaicing are two important techniques used in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to create accurate and detailed maps. An orthophoto is an aerial photograph that has been adjusted to remove any distortion caused by the angle of the camera or terrain. This adjustment results in a map-like image that can be used for accurate measurements and analysis. Mosaicing, on the other hand, involves combining multiple images into a single, seamless image to create a complete picture of a larger area.
One of the main advantages of orthophotos and mosaics is their high level of accuracy. By removing distortion and combining multiple images, GIS professionals can create highly detailed maps that accurately represent the landscape. This level of accuracy is crucial for a wide range of applications, including urban planning, natural resource management, and disaster response. For example, orthophotos can be used to measure distances, areas, and angles with great precision, while mosaics provide a complete view of a large area that may not be visible in a single image.
Orthophotos and mosaics are also incredibly useful for visualizing and analyzing spatial data. By overlaying other GIS data, such as land use classifications or infrastructure locations, on top of orthophotos and mosaics, researchers and planners can gain a deeper understanding of the spatial relationships within a given area. This visual analysis can reveal patterns and trends that may not be apparent in tabular data alone, allowing for more informed decision-making.
In conclusion, orthophoto and mosaicing are essential tools in GIS that enable accurate mapping, visualization, and analysis of spatial data. Their high level of accuracy and ability to create detailed and seamless images make them invaluable for a wide range of applications in diverse fields. By leveraging the power of orthophotos and mosaics, GIS professionals can better understand and manage the complex spatial relationships that exist in our world.