-
- HOME
- ABOUT US
- SOLUTION
- PROJECTS
- INDUSTRIES
- CLIENT NETWORK
- CAREER
- CONTACT WooCommerce not Found
- Newsletter
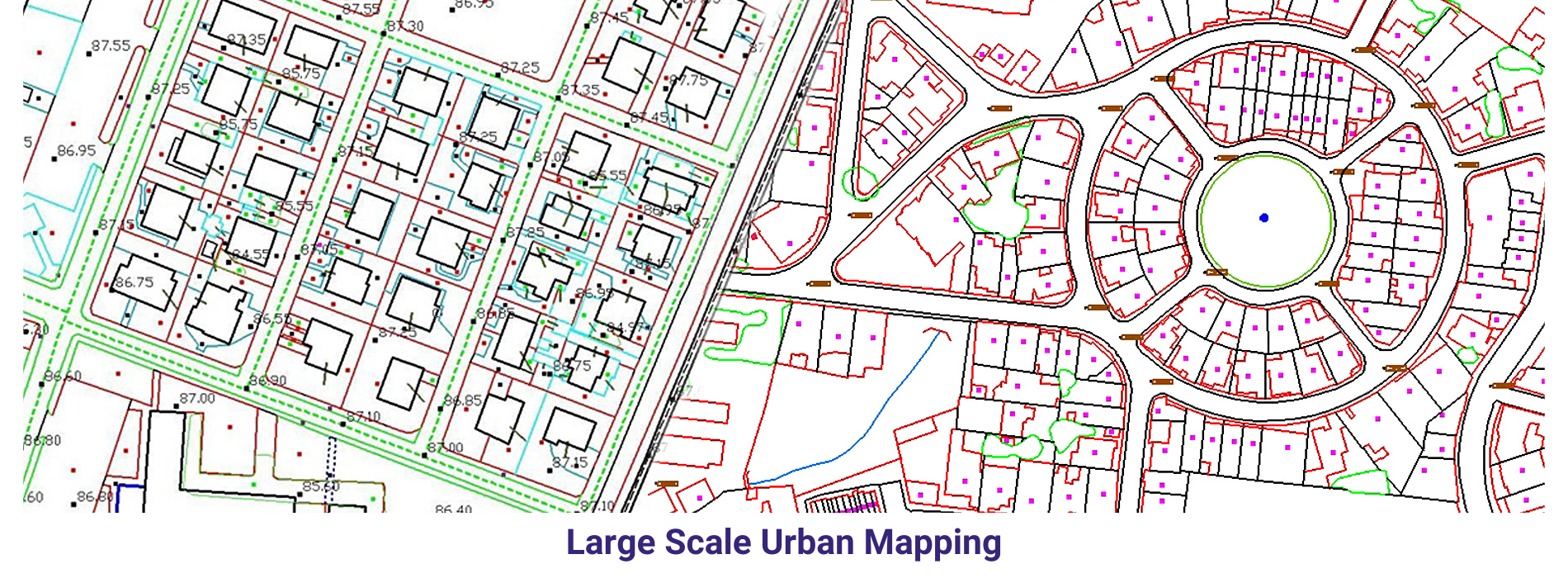
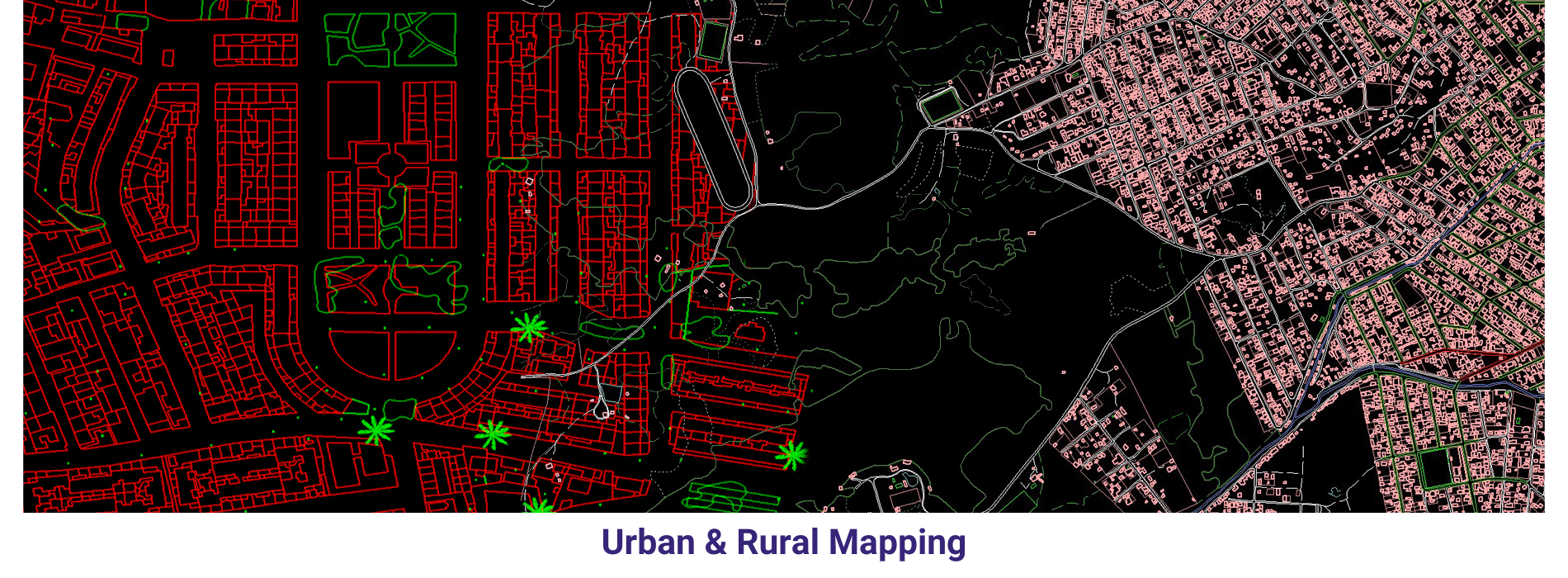
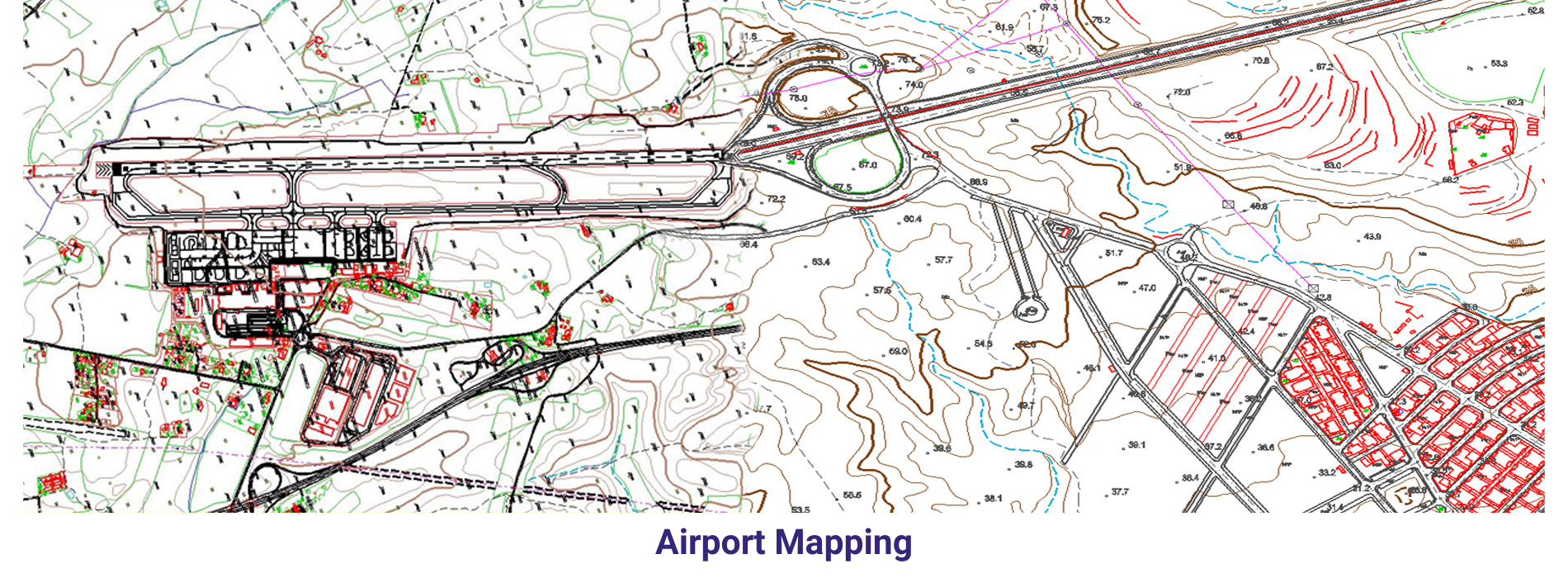
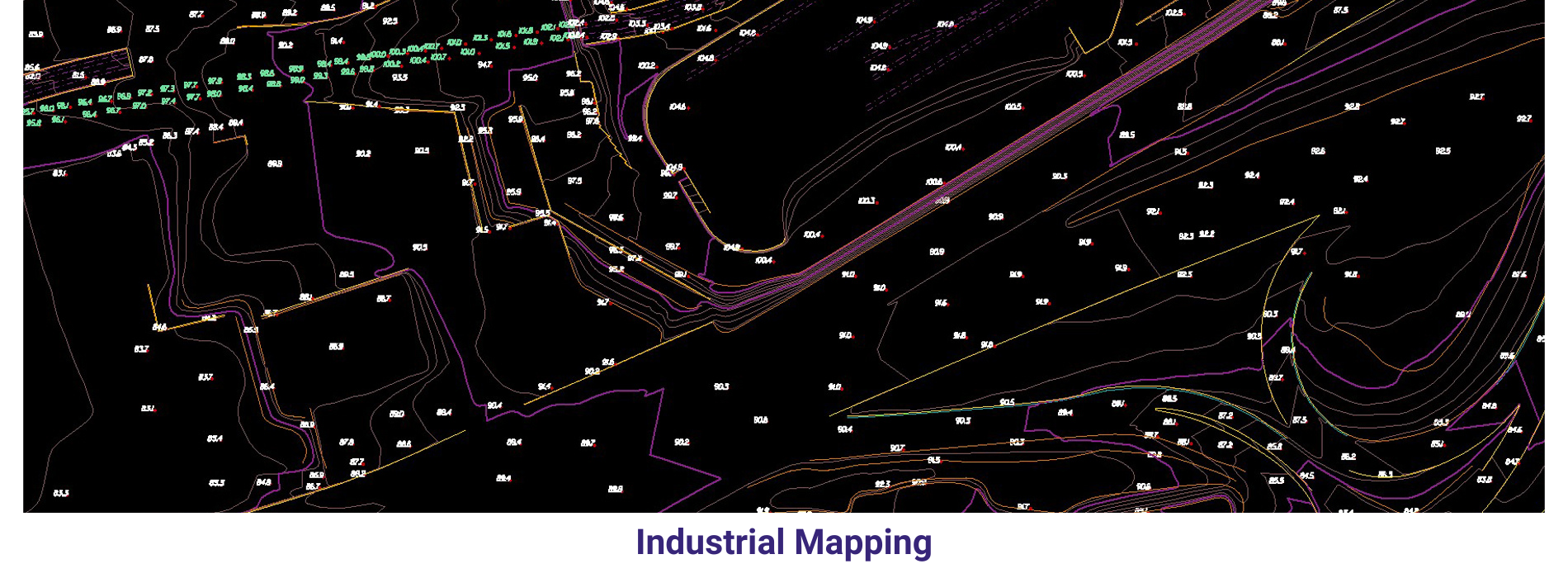
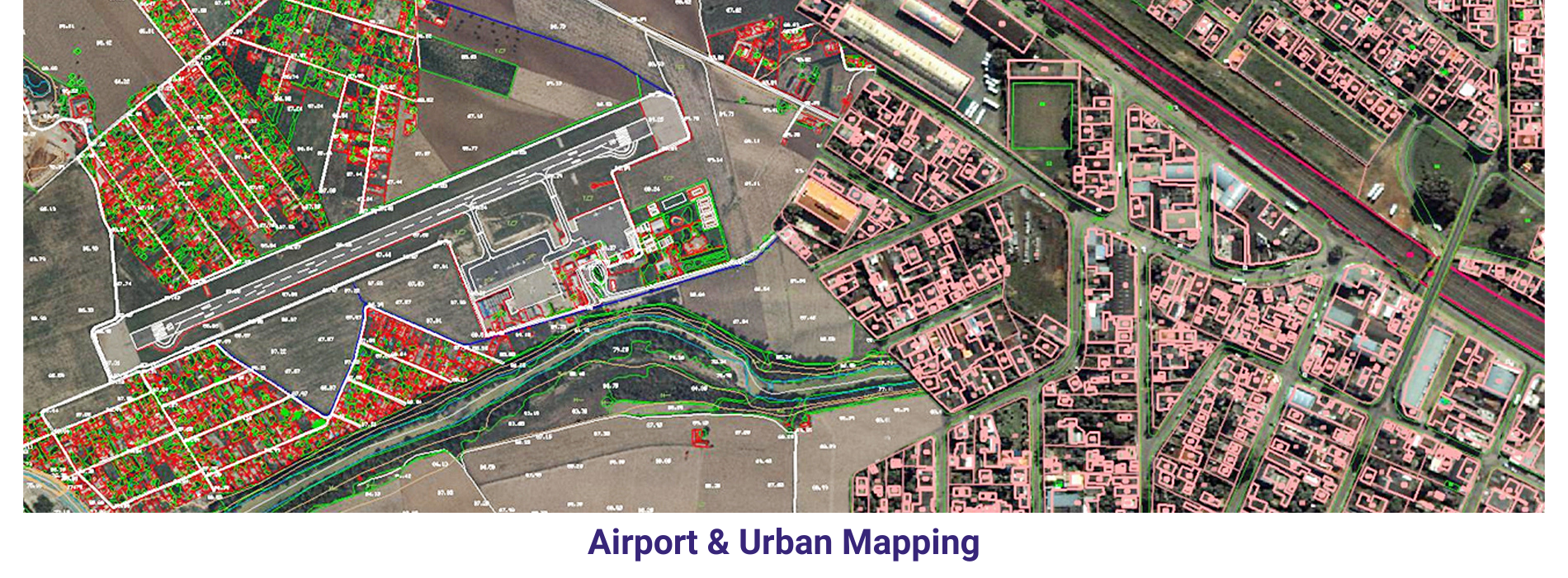
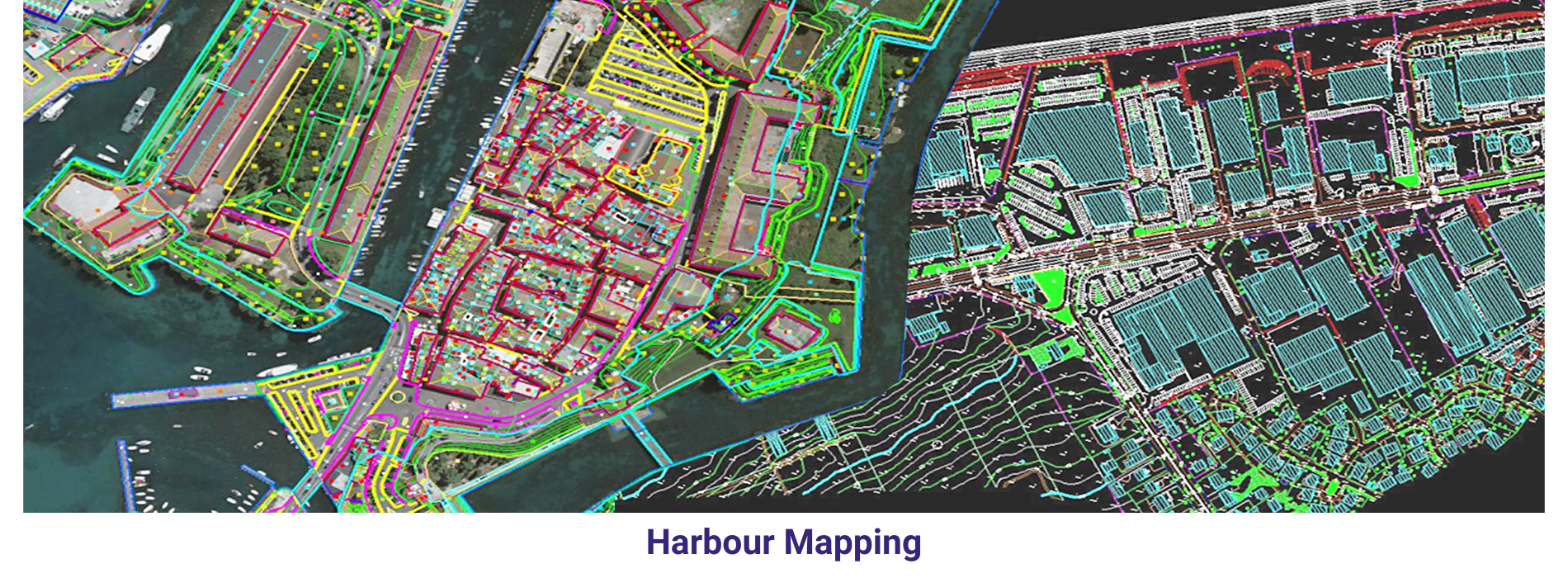
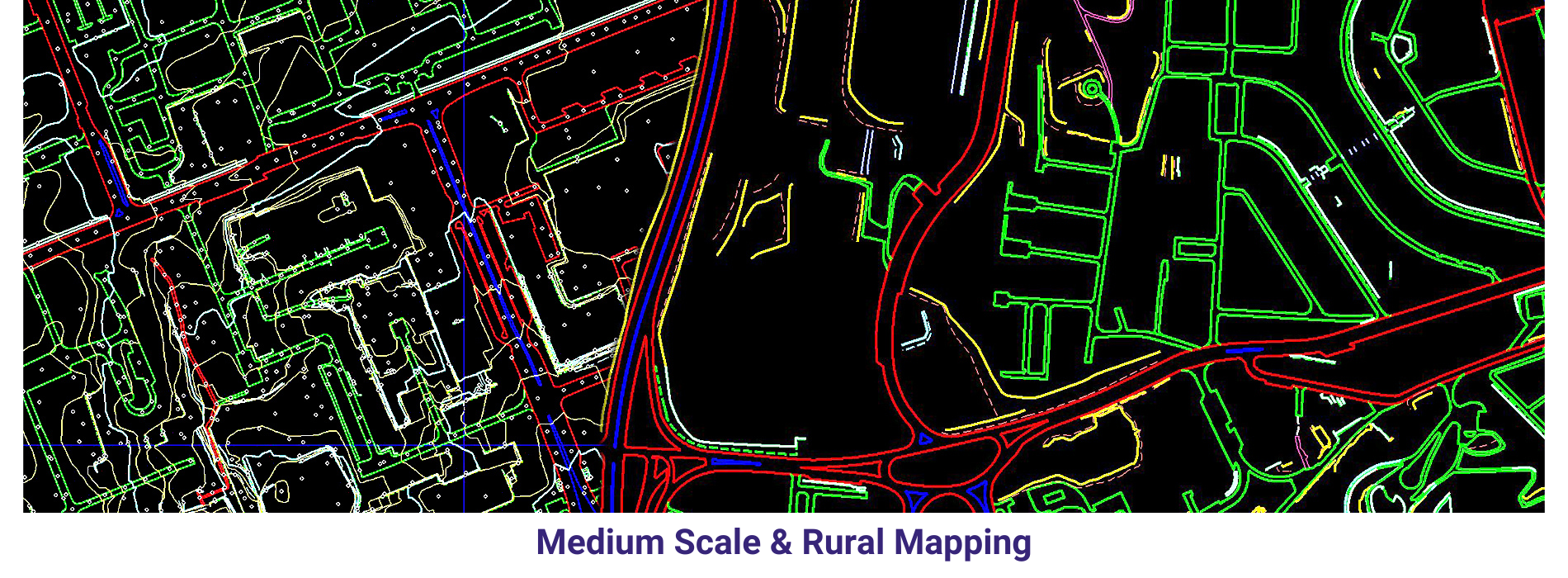
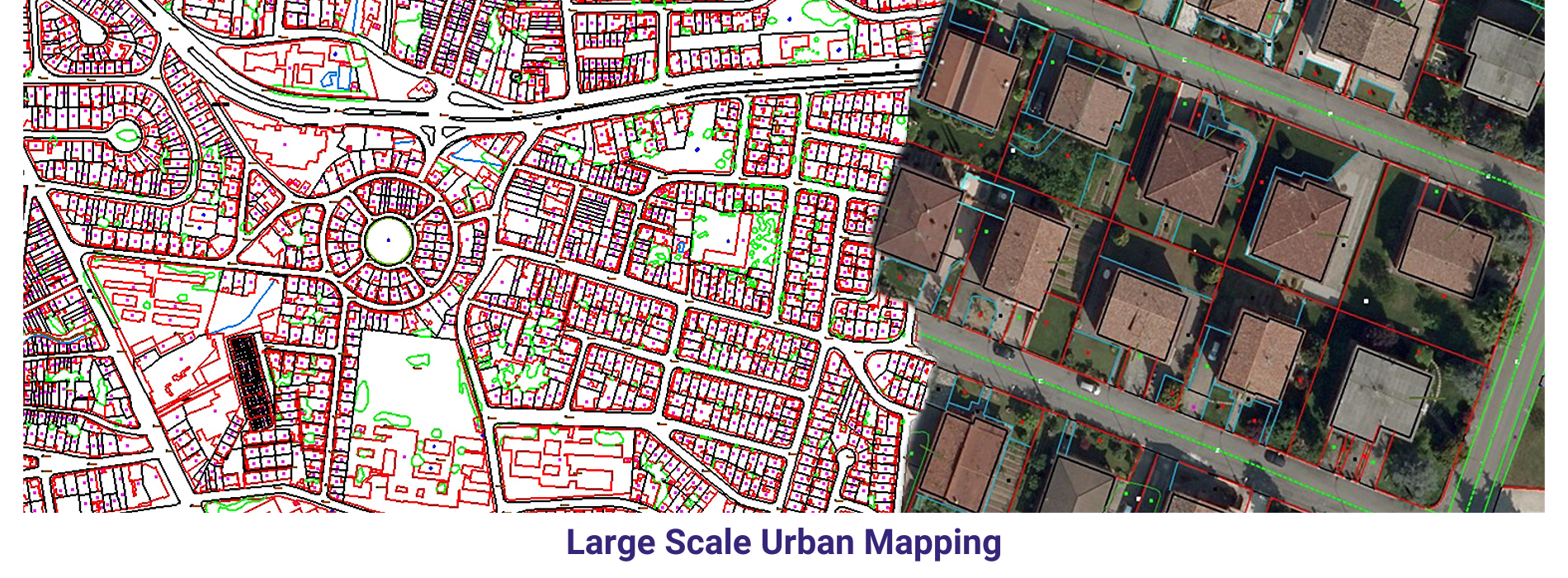
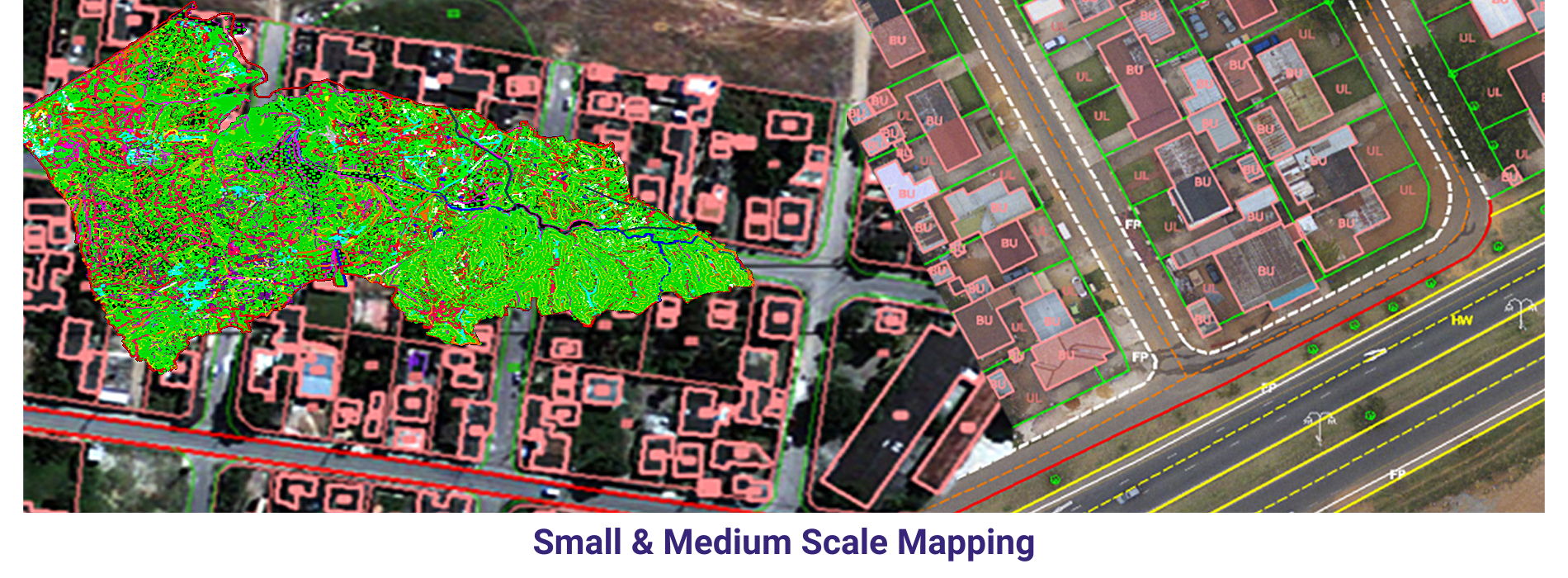

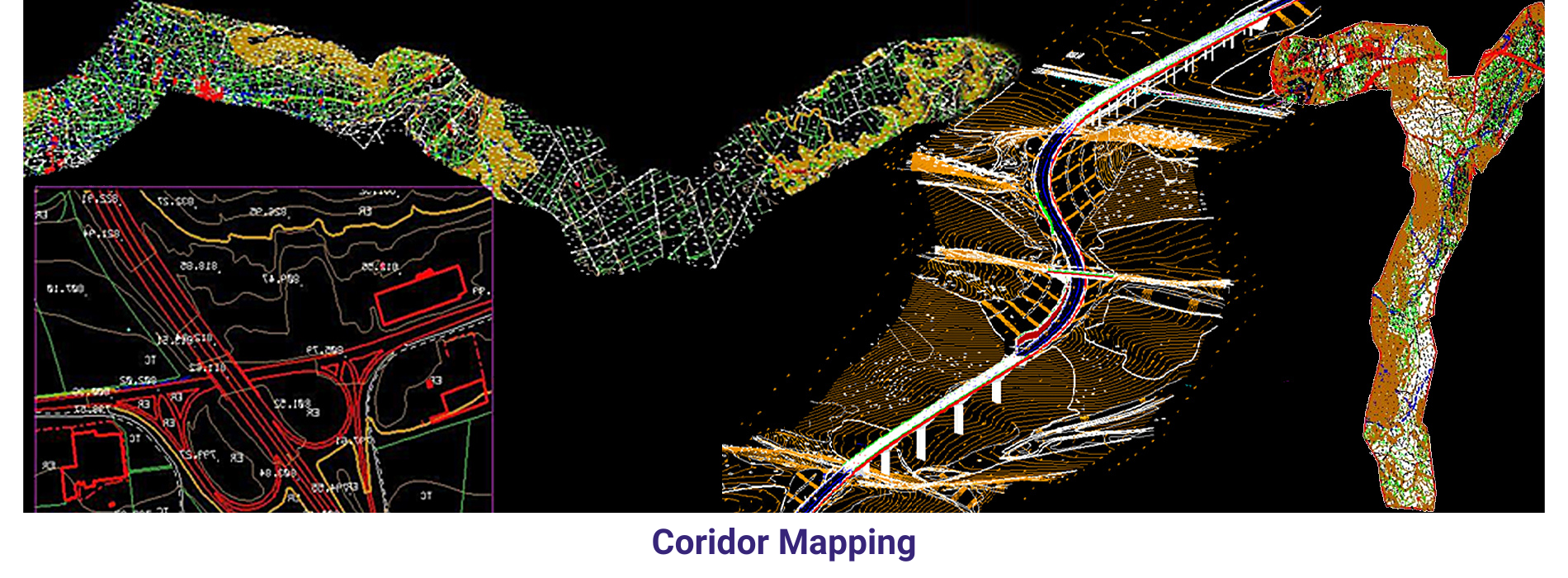
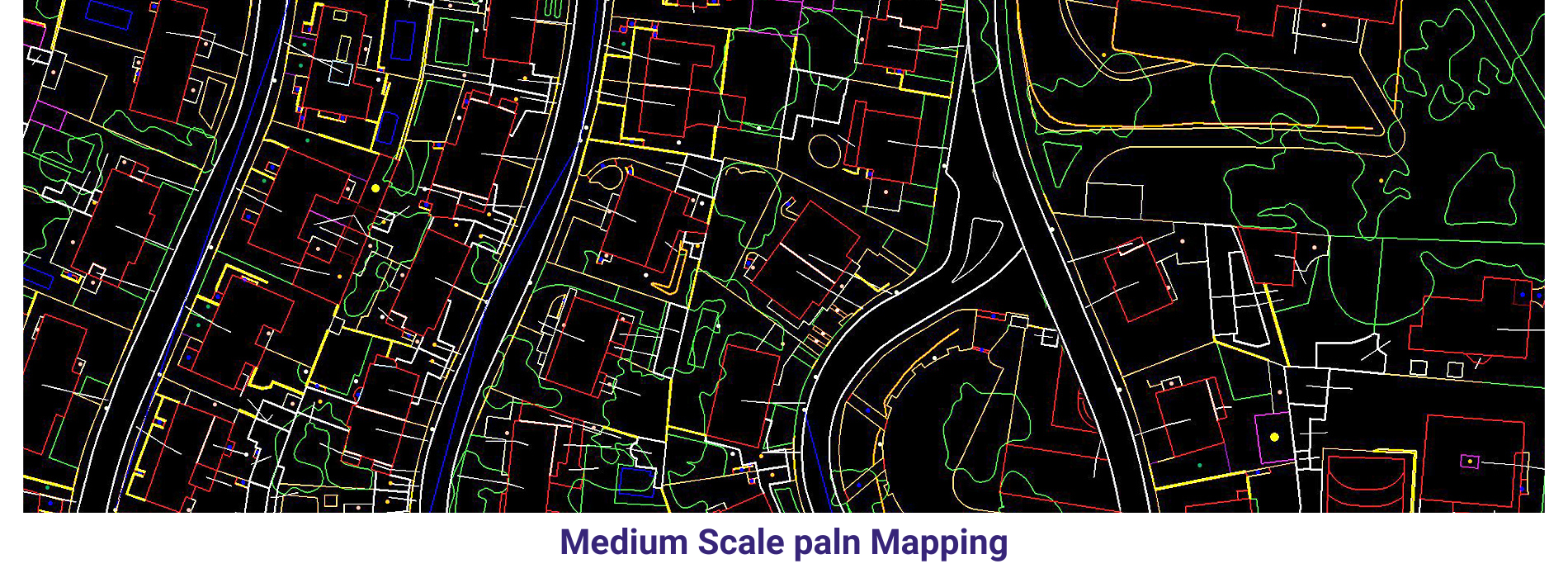












AAMGST personnel are well acquitted with the mapping standards (ASPRS, NMAS, and NSSDA). Our dedicated team has been involved in delivering the client’s expected quality with on time delivery.
AAMGST has been produced parametric data for Europe, US, Middle East and Latin American countries with different projections (UTM wgs84, Sardinia Ixal coordinate system, State plane coordinate system).
Large Scale mapping _ Aerial: We have delivered 20000 hectors of large scale cartographic data with 1:500 scale for Lugo area in Spain and 1:1000 scale for Italia. The purpose of the project is to monitor the changes / obstacles around the airport and its surrounding area.
Medium scale mapping _Arial: We delivered 75000 hectors of Urban parametric data to our clients by using our own automation methods in photogrammetry discipline.
Small scale mapping _ Aerial and Satellite : we have mapped 4.5 million hectors (115000) with cartographic data from Satellite stereo pairs and Aerial imagery. The of the project is to monitor forest inventory for Brazil oil company.
3D cartography in GIS (Geographic Information Systems) is a cutting-edge technology that allows for the creation of three-dimensional representations of geographical data. This technology not only enhances the visual appeal of maps but also provides a more realistic and immersive representation of spatial information. By incorporating elevation data, 3D cartography allows users to visualize landscapes, buildings, and other features in a way that is closer to real life, making it easier to interpret and understand complex spatial relationships.
One of the key advantages of 3D cartography in GIS is its ability to provide more accurate and detailed representations of the physical world. By adding a vertical dimension to traditional two-dimensional maps, users can gain a better understanding of the topography and terrain of a region. This can be particularly useful in applications such as urban planning, where accurate representations of buildings and infrastructure are essential for making informed decisions. Furthermore, 3D cartography can help to improve the accuracy of spatial analysis and modeling by providing a more complete picture of the spatial relationships between different geographic features.
In addition to its practical applications, 3D cartography also has the potential to enhance the visual appeal of maps and geographical information. By creating realistic and visually engaging representations of geographical data, 3D cartography can help to increase user engagement and improve the effectiveness of communication. This can be especially useful in fields such as environmental science and tourism, where the visualization of landscapes and natural features is important for conveying information to a wider audience. Overall, 3D cartography in GIS is a powerful tool that has the potential to revolutionize the way we visualize and interpret spatial information.
In conclusion, 3D cartography in GIS offers a range of benefits in terms of accuracy, visualization, and communication. By incorporating elevation data and creating three-dimensional representations of geographical data, this technology provides a more realistic and immersive understanding of spatial relationships. With its ability to enhance the accuracy of maps and improve the visual appeal of geographical information, 3D cartography has the potential to revolutionize the field of GIS and open up new possibilities for spatial analysis and modeling. As technology continues to advance, 3D cartography in GIS will likely play an increasingly important role in shaping how we perceive and interact with the world around us.