-
- HOME
- ABOUT US
- SOLUTION
- PROJECTS
- INDUSTRIES
- CLIENT NETWORK
- CAREER
- CONTACT WooCommerce not Found
- Newsletter
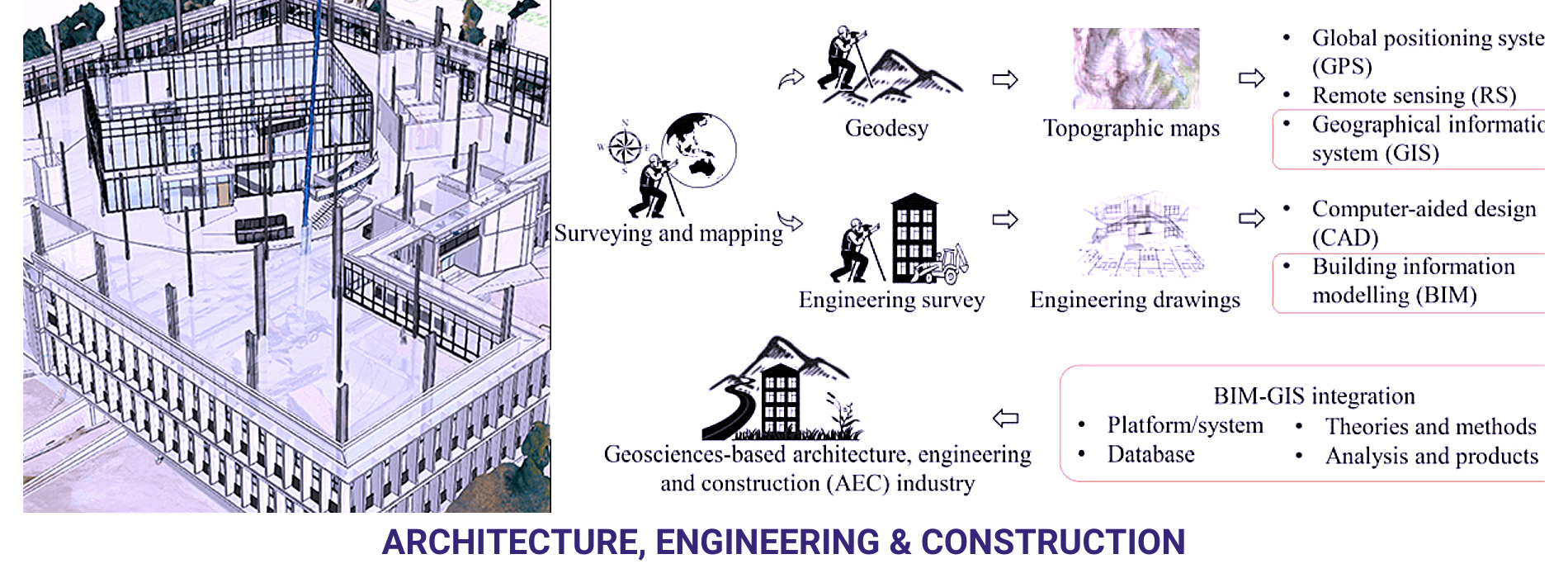


Site Analysis and Planning: Before any construction can begin, it’s essential to understand the site’s topography, geology, and other environmental factors. Geospatial technologies like Global Positioning Systems (GPS), Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR), and aerial photography can provide detailed maps and 3D models of the site, allowing architects and engineers to plan projects more effectively.
Construction and Surveying: During construction, geospatial technologies are used for surveying, grading, and layout. High-precision GPS and robotic total stations can be used to ensure that structures are built according to plan and within the specified tolerances. These tools also help in monitoring construction progress and identifying potential issues before they become costly problems.
Infrastructure Management: Once a project is complete, geospatial technology can be used to manage and maintain infrastructure. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) can store and analyse data about roads, bridges, and other infrastructure assets, helping to plan maintenance and repairs more effectively.