-
- HOME
- ABOUT US
- SOLUTION
- PROJECTS
- INDUSTRIES
- CLIENT NETWORK
- CAREER
- CONTACT WooCommerce not Found
- Newsletter


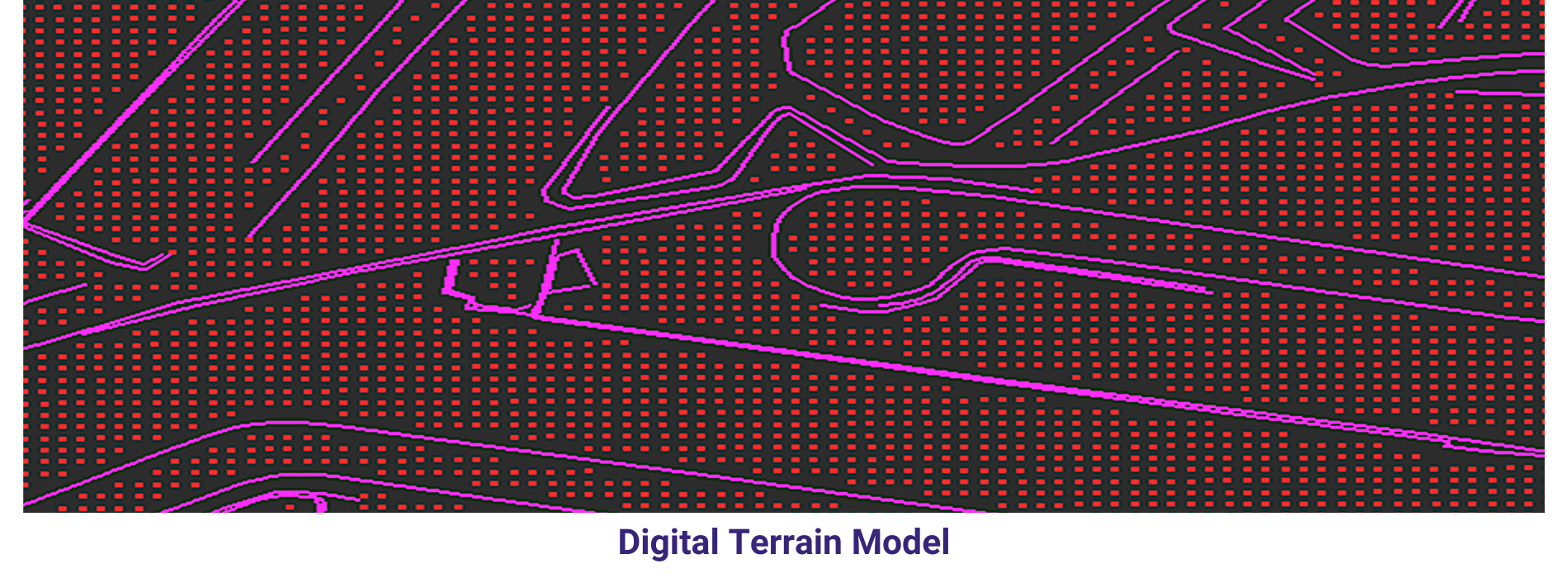
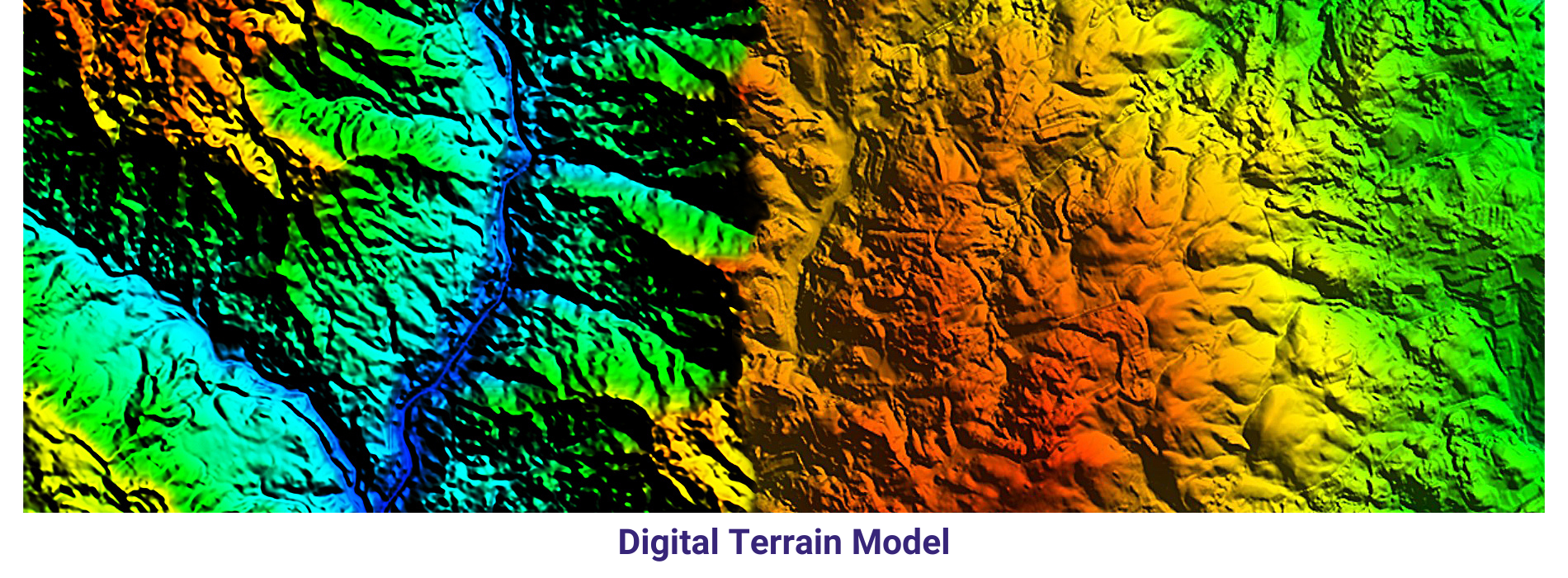
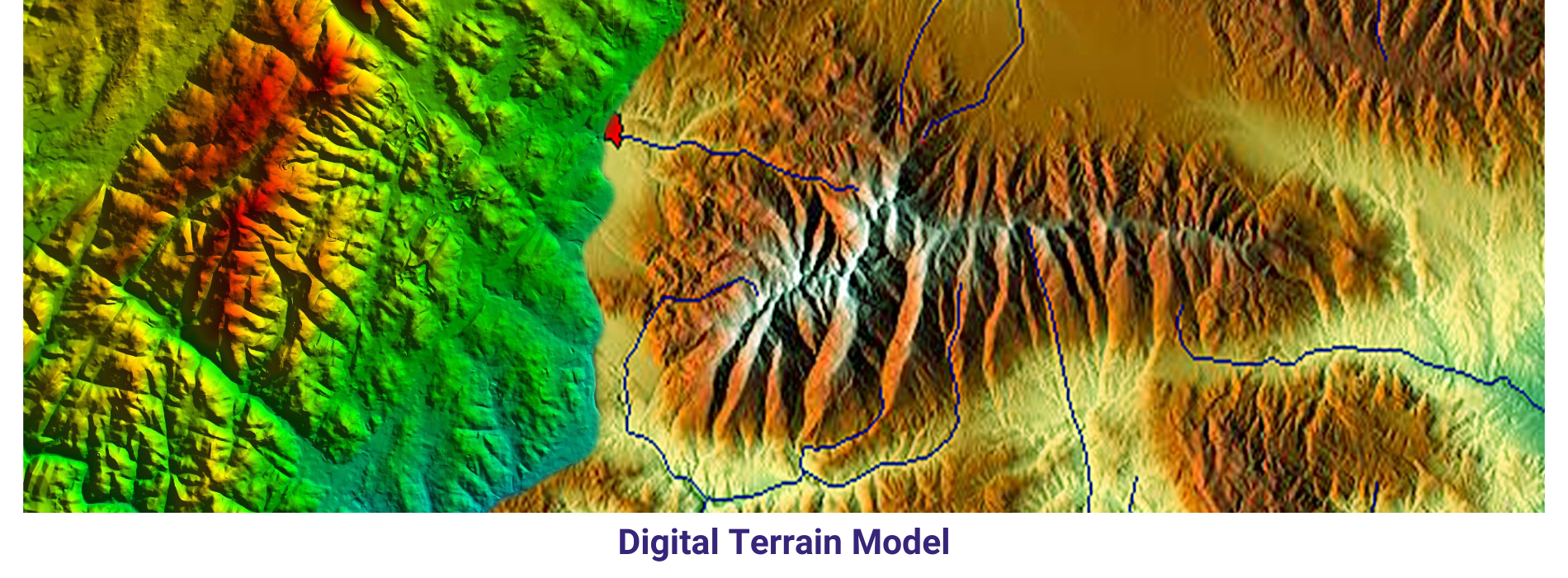
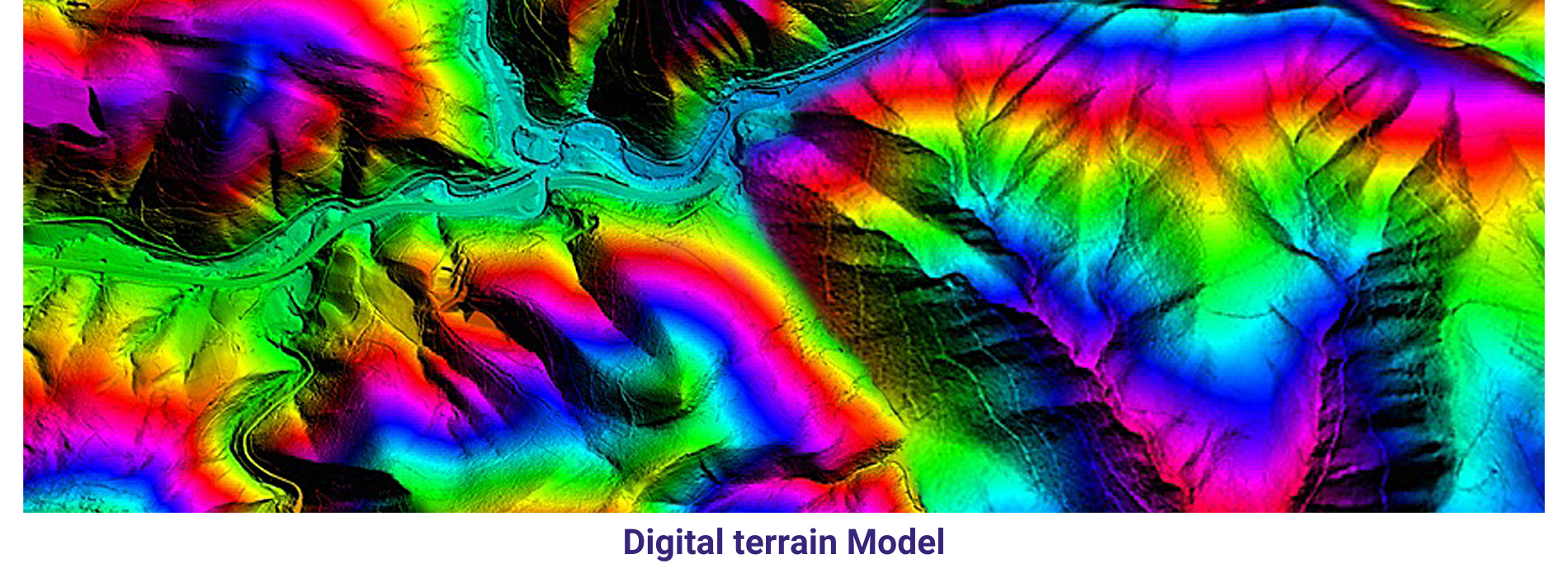









AAM Geo Spatial Tech Private Limited is capable of producing high resolution Digital Terrain Models. Our experienced team can able to produce accurate data with cost-efficient methods for client’s planning and decision making. AAMGST staff is expertise in placement of break lines at required place only and team skills have been upgraded as per the latest available technologies. We follow in-house developed quality check programmes and procedures to exceed the client requirement. Our photogrammetry team members are experts in manual contours. Final DTM data has been submitted in different formats line ASCII, TIN, ESRI ASCII grid and GeoTiff, Img.
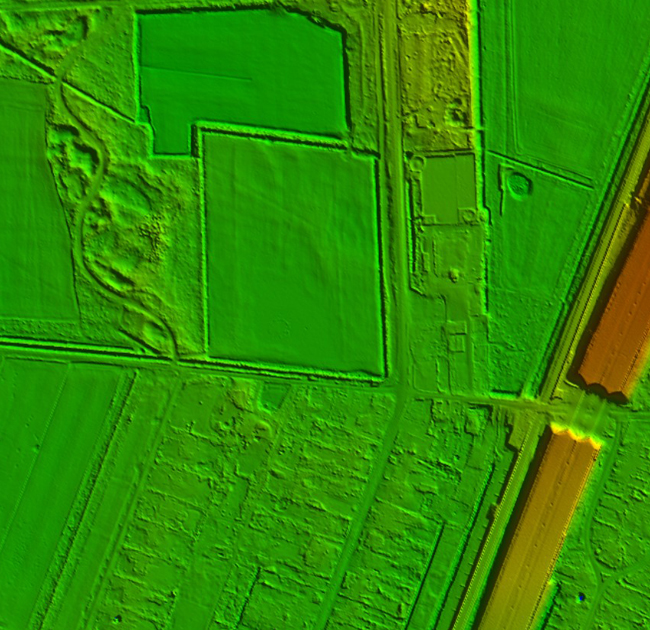
A Digital Terrain Model (DTM) is a digital representation of the bare earth surface, devoid of any surface features such as buildings, vegetation, or other structures. It provides elevation data for each point on the terrain, allowing for the creation of a detailed three-dimensional model of the Earth’s surface.
DTMs are typically derived from various remote sensing technologies, including LiDAR, radar, or photogrammetry. These technologies capture elevation information by measuring the distance between the sensor and the Earth’s surface, allowing for the creation of high-resolution elevation models.
Overall, Digital Terrain Models are valuable geospatial datasets that provide essential information about the Earth’s surface, supporting a wide range of applications across different disciplines and industries.

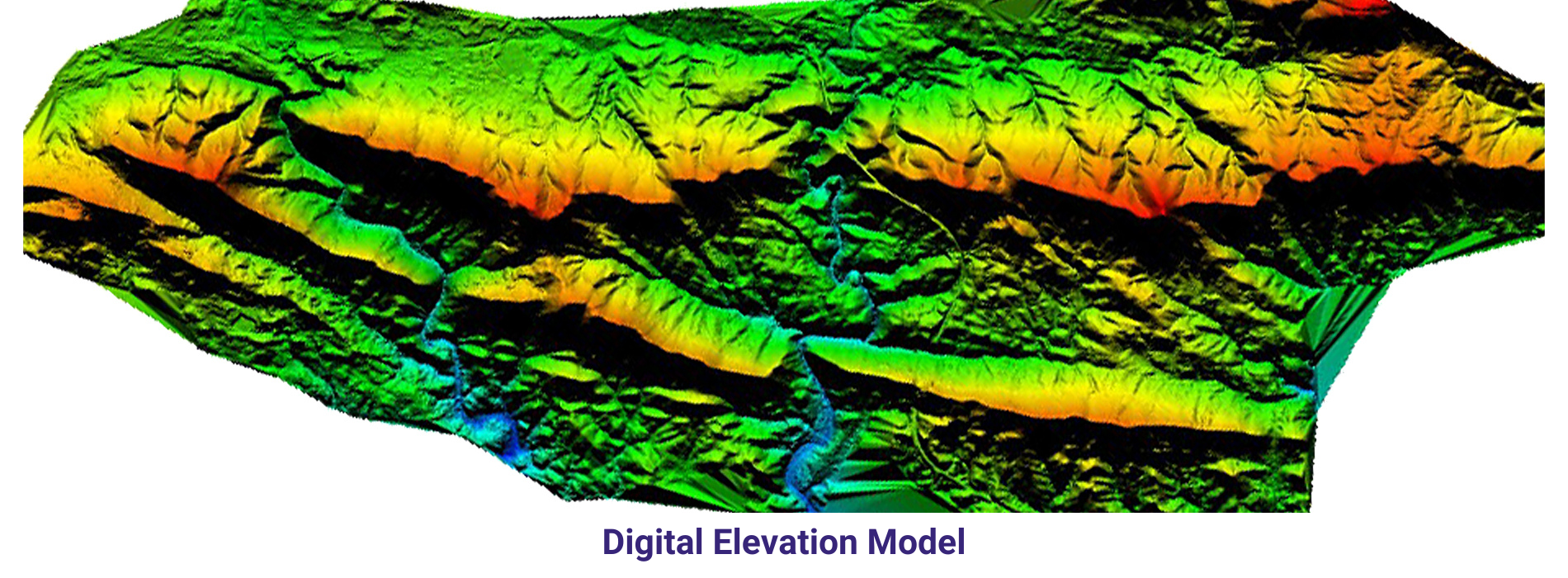
A Digital Elevation Model (DEM) is a digital representation of the Earth’s surface that provides elevation data for each point on a grid, typically arranged in a raster format. Unlike a Digital Terrain Model (DTM), which represents only the bare earth surface without any surface features, a DEM includes both terrain and any surface features such as buildings, vegetation, and other structures.
DEM data is commonly derived from various remote sensing technologies, including LiDAR, radar, photogrammetry, and satellite imagery. These technologies capture elevation information by measuring the distance between the sensor and the Earth’s surface, allowing for the creation of detailed elevation models.
Overall, Digital Elevation Models are valuable geospatial datasets that provide essential information about the Earth’s surface, supporting a wide range of applications across different disciplines and industries.

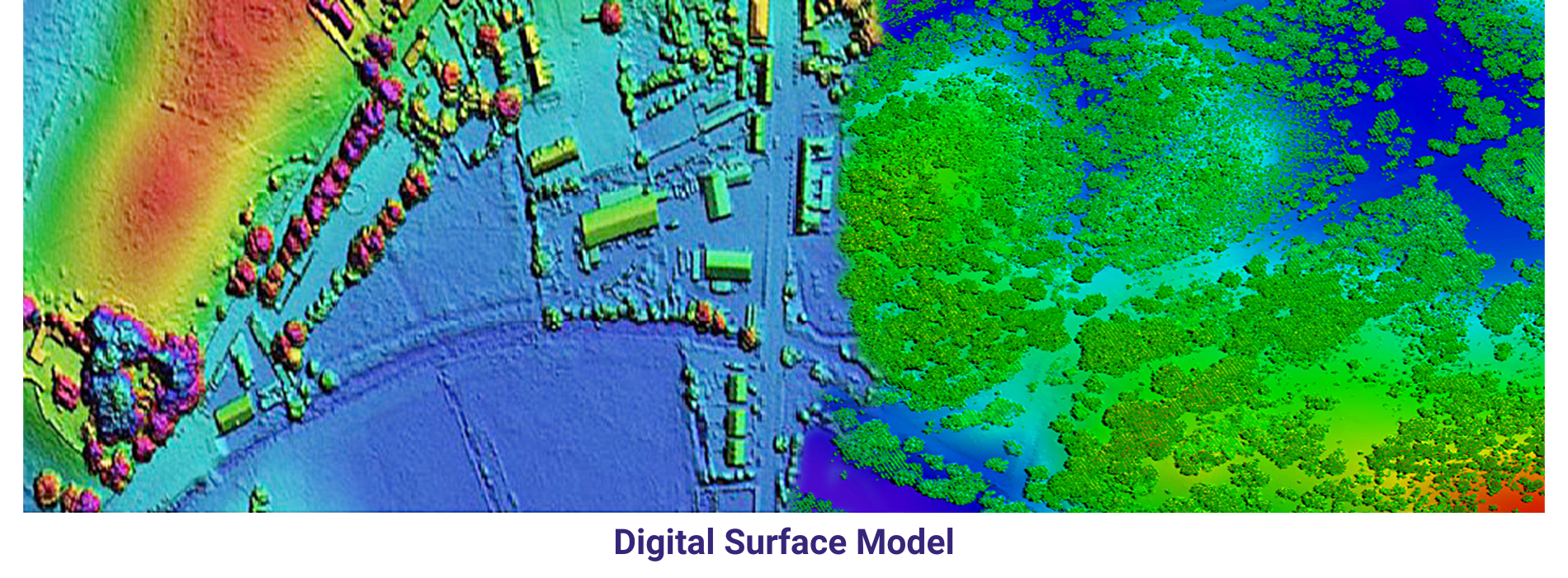
A Digital Surface Model (DSM) is a digital representation of the Earth’s surface as observed by a sensor or observer, including all surface features such as buildings, vegetation, and other objects. Unlike a Digital Terrain Model (DTM), which represents the bare earth surface without any objects, a DSM includes these surface features in addition to the bare terrain.
DSMs are typically derived from remote sensing data sources such as aerial photography, satellite imagery, or LiDAR data. These data sources provide elevation information for each point on the Earth’s surface, allowing for the creation of a detailed three-dimensional model that accurately reflects the terrain and surface features.
Overall, Digital Surface Models are powerful geospatial datasets that provide detailed and comprehensive information about the Earth’s surface, enabling a wide range of applications in diverse fields.
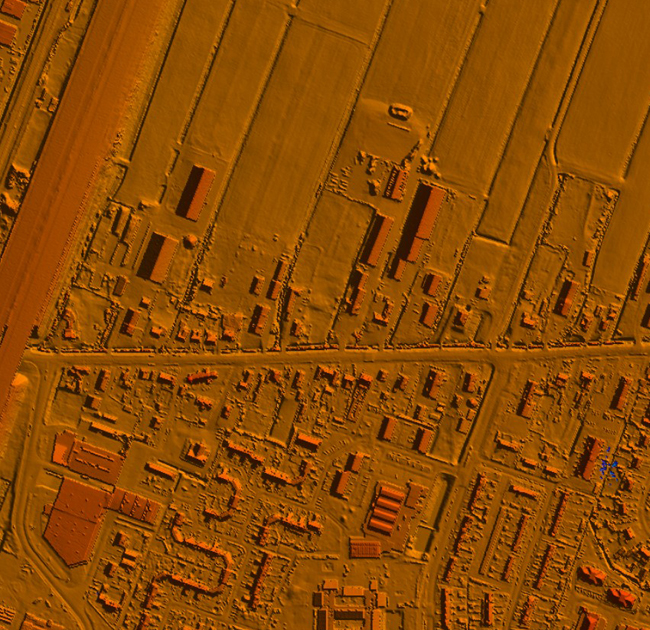
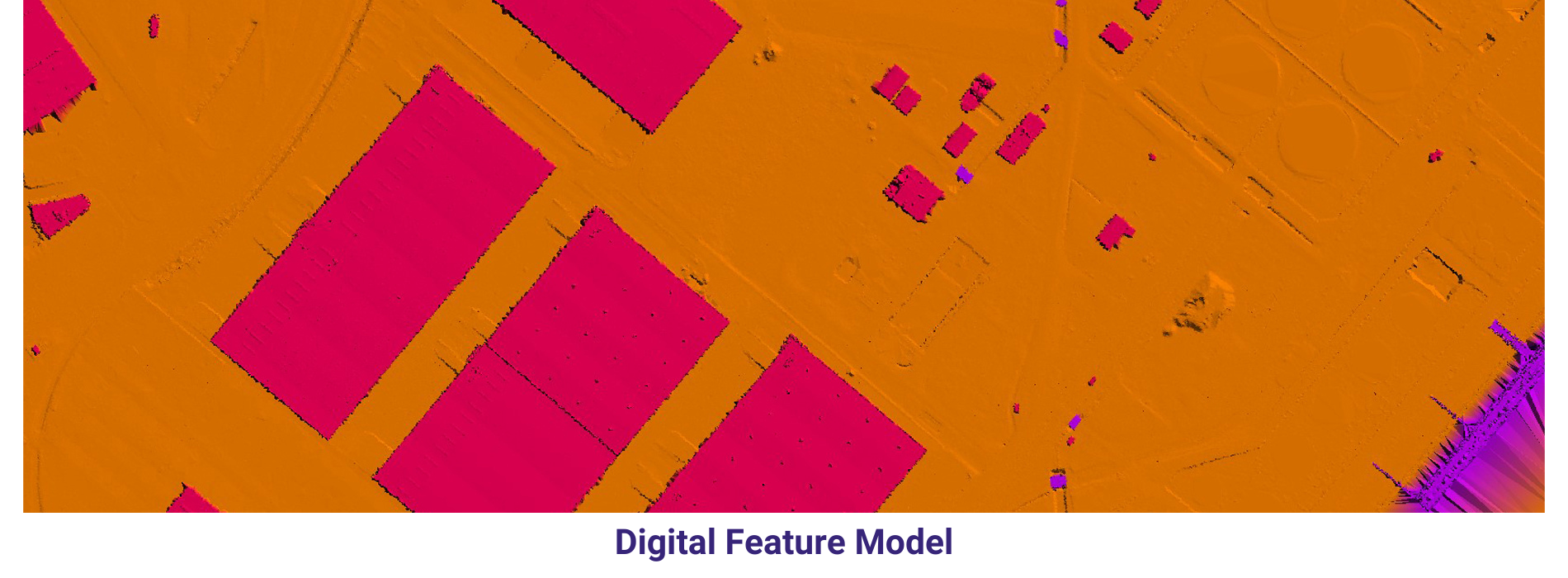
A Digital Feature Model (DFM) is a representation of the features of a terrain or environment in a digital format. It is used in various fields such as civil engineering, urban planning, and geographic information systems (GIS) to model and analyze the physical and spatial characteristics of the Earth’s surface.
The data can be collected through a variety of methods, including aerial and satellite imagery, ground surveys, and GPS technology.
In summary, a Digital Feature Model is a comprehensive representation of the features of a terrain or environment, which is used for a wide range of applications in civil engineering, urban planning, and geographic information systems. It is created using GIS software and integrates different types of spatial data to provide a detailed and accurate model of the Earth’s surface.
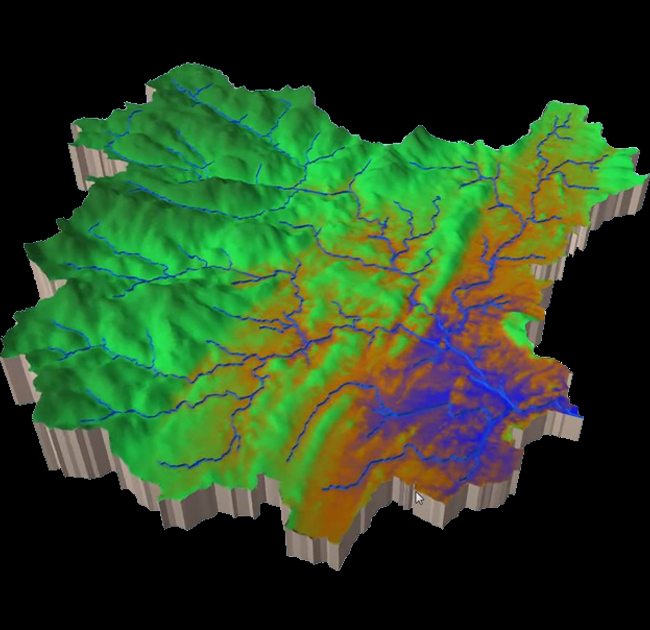
A 3D surface model is a digital representation of the Earth’s surface that captures its three-dimensional geometry and spatial characteristics. Unlike traditional 2D maps or elevation models, which represent terrain in two dimensions (latitude and longitude, plus elevation), 3D surface models provide a more immersive and detailed depiction of the landscape.
Overall, 3D surface models offer a powerful tool for visualizing, analyzing, and understanding the Earth’s surface in three dimensions, with applications spanning a wide range of fields and industries.
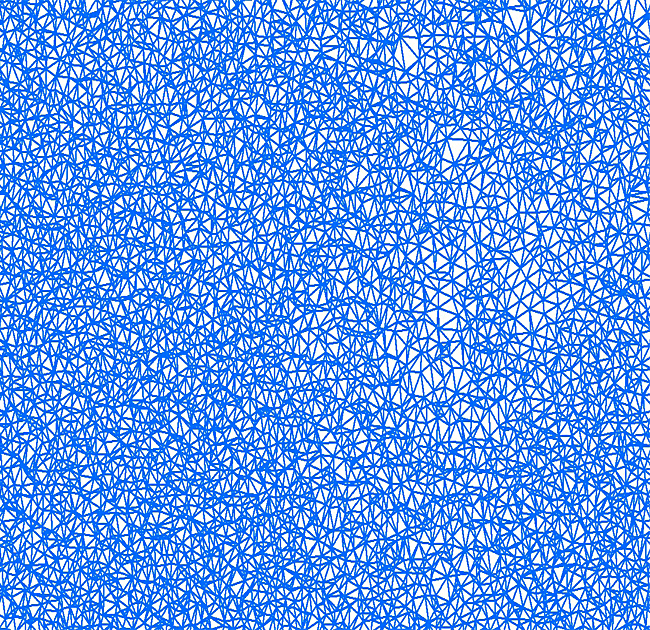
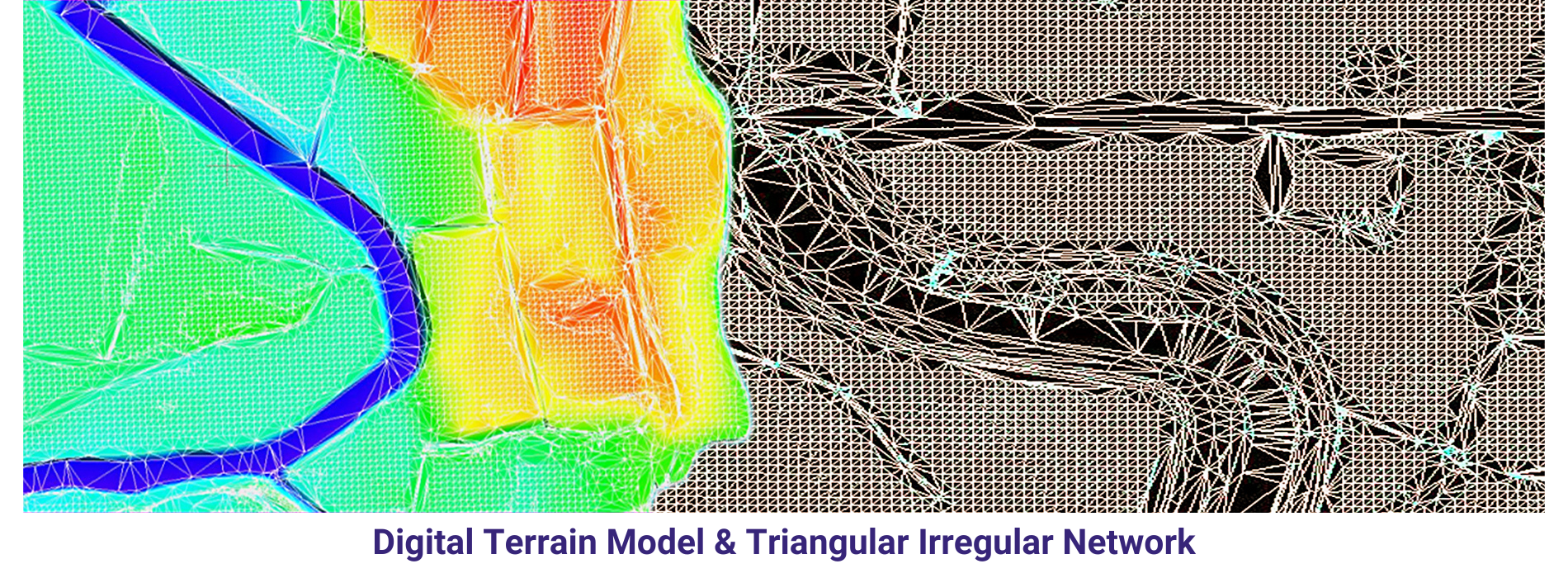
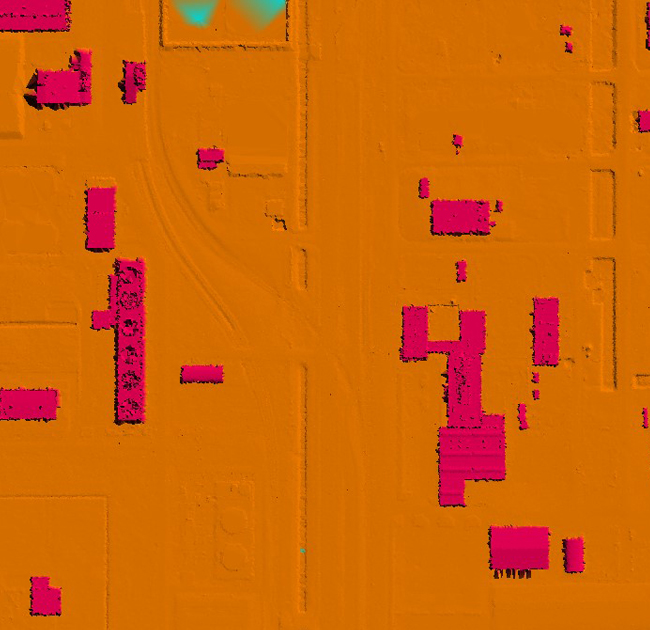
A Triangulated Irregular Network (TIN) is a type of surface model used in GIS (Geographic Information Systems) and terrain analysis to represent three-dimensional surfaces. It is composed of a set of non-overlapping triangles that cover the terrain, where each triangle is defined by three vertices and represents a local approximation of the surface.
Overall, Triangulated Irregular Networks are valuable tools for representing and analysing terrain surfaces, providing a flexible and accurate representation of three-dimensional landscapes in GIS and terrain modelling applications.
