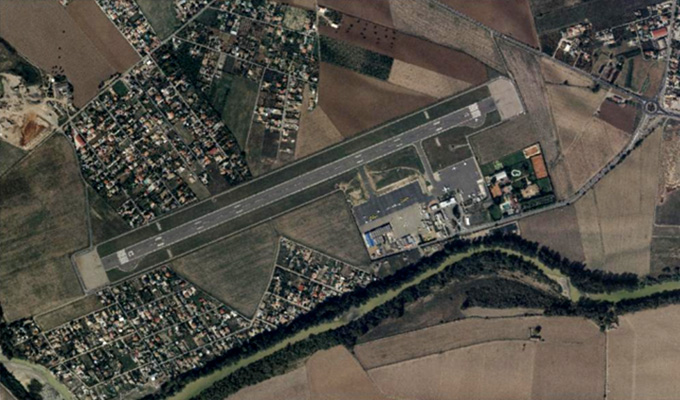
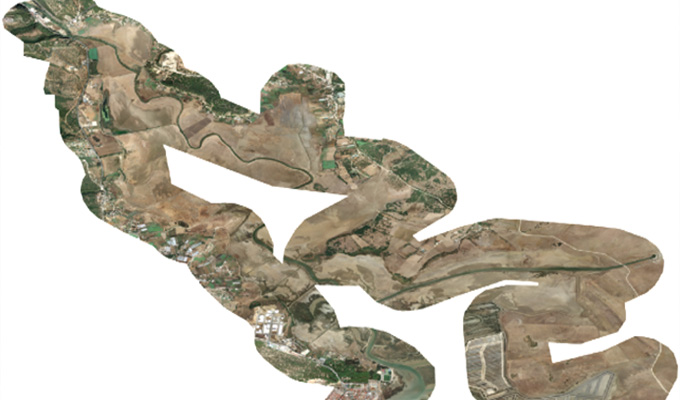
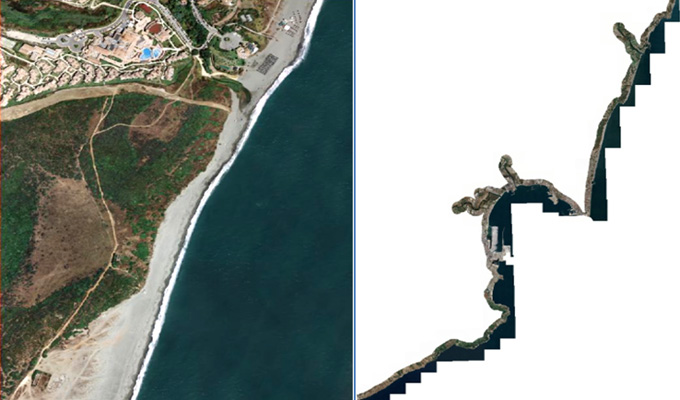
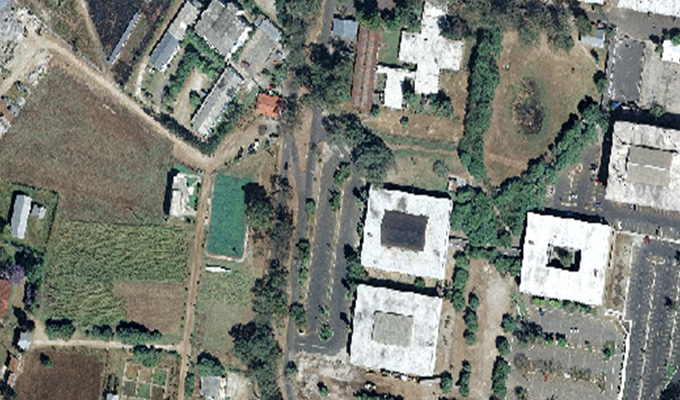



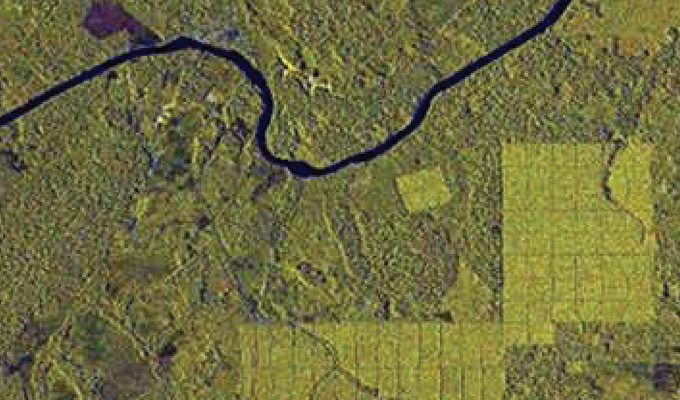


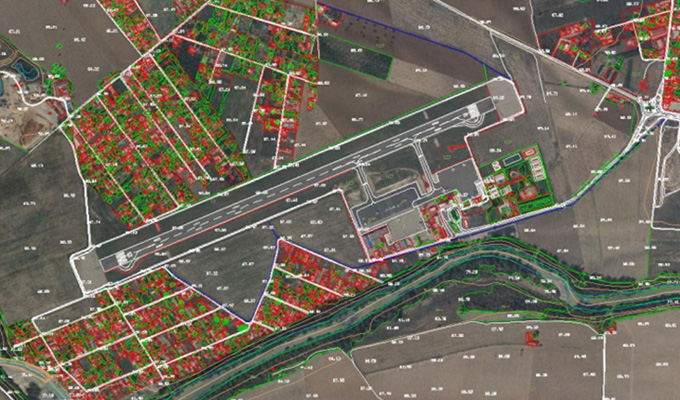






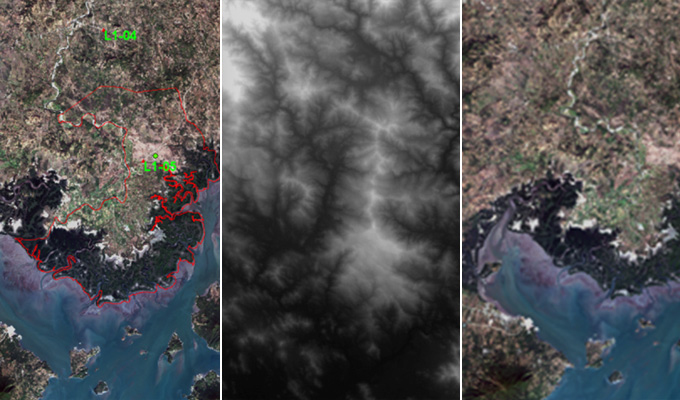
Orthophoto Mosaic
In order to keep pace with ongoing competition, AAMGST is constantly innovating to find newer solutions, technologies, and methodologies that can help our clients to ensure higher quality.
AAMGST has delivered orthophotos from aerial frames (30,000) and 1.5 million Sqkm from satellite data. Orthophotos with high accuracy and radiometrically enhanced from different sensors (aerial frame, digital camera, ADS40, and satellite) with various GSDs (0.08, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, and 1.0 meters).
By following all the standards of FGDC, we have generated orthophotos (from multiband images) by adopting the best practices in production and quality checking.
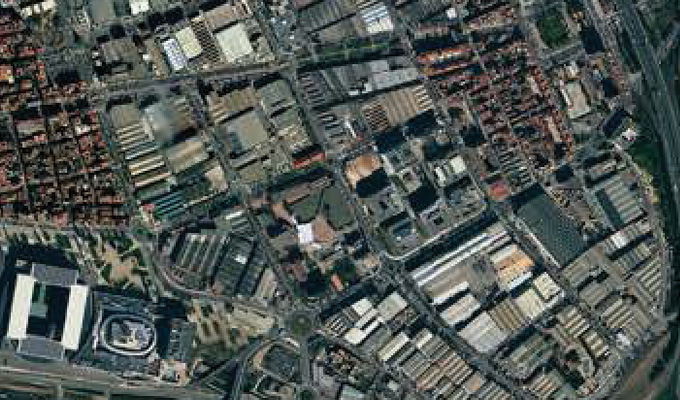
Orthophoto and Mosaicing are two important techniques used in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to create accurate and detailed maps. An orthophoto is an aerial photograph that has been adjusted to remove any distortion caused by the angle of the camera or terrain. This adjustment results in a map-like image that can be used for accurate measurements and analysis. Mosaicing, on the other hand, involves combining multiple images into a single, seamless image to create a complete picture of a larger area.
One of the main advantages of orthophotos and mosaics is their high level of accuracy. By removing distortion and combining multiple images, GIS professionals can create highly detailed maps that accurately represent the landscape. This level of accuracy is crucial for a wide range of applications, including urban planning, natural resource management, and disaster response. For example, orthophotos can be used to measure distances, areas, and angles with great precision, while mosaics provide a complete view of a large area that may not be visible in a single image.
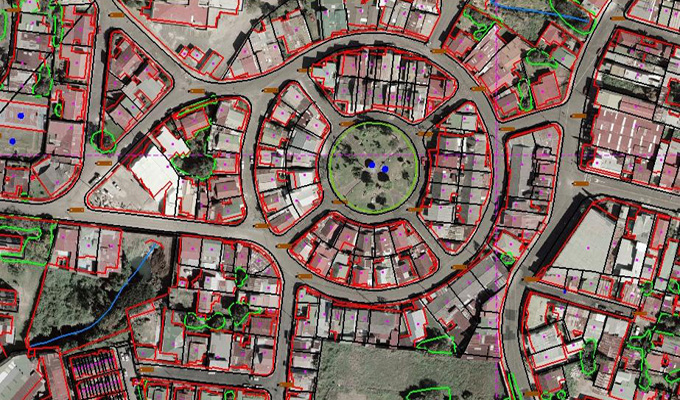
Orthophotos and mosaics are also incredibly useful for visualizing and analyzing spatial data. By overlaying other GIS data, such as land use classifications or infrastructure locations, on top of orthophotos and mosaics, researchers and planners can gain a deeper understanding of the spatial relationships within a given area. This visual analysis can reveal patterns and trends that may not be apparent in tabular data alone, allowing for more informed decision-making.
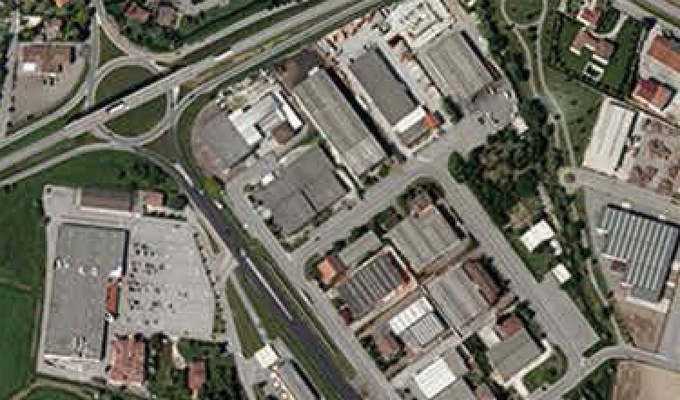
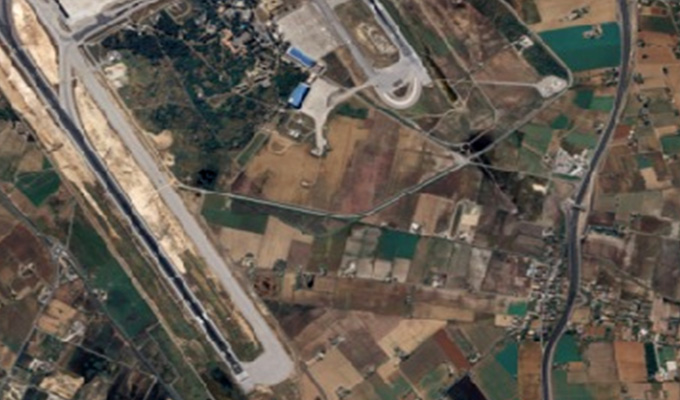
Aerial Orthophotos
Aerial orthophotos are high-resolution images of the Earth's surface captured from aircraft equipped with specialized cameras. These images undergo processing to correct distortions caused by factors such as terrain relief, camera tilt, and perspective, resulting in a uniform scale and accurate representation of the terrain. Overall, aerial orthophotos are valuable assets in the geospatial industry, providing accurate and detailed imagery for a wide range of applications, from urban planning and environmental management to emergency response and infrastructure development. Their high resolution, geometric accuracy, and wide coverage make them indispensable tools for visualizing, analyzing, and managing spatial data.
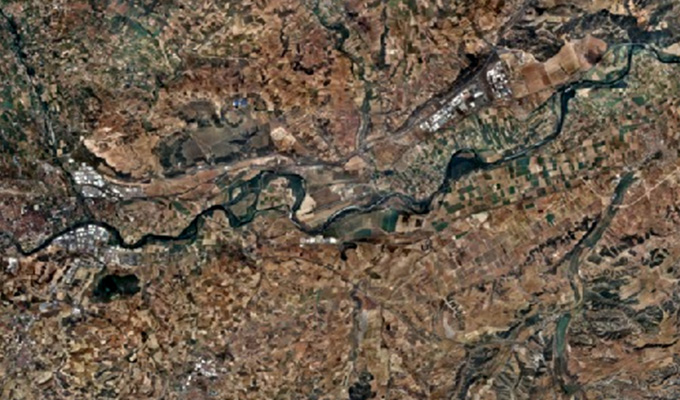
Satellite Orthophotos
Satellite orthophotos are high-resolution images of the Earth's surface captured by remote sensing satellites orbiting the Earth. These images undergo processing to correct distortions caused by factors such as terrain relief, satellite motion, and atmospheric conditions, resulting in a uniform scale and accurate representation of the terrain. Overall, satellite orthophotos are valuable assets in the geospatial industry, providing accurate and detailed imagery for a wide range of applications, from environmental monitoring and resource management to disaster response and scientific research. Their global coverage, high resolution, and temporal capabilities make them indispensable tools for visualizing, analyzing, and managing spatial data on a global scale.
Drone Orthophotos
Drone orthophotos, also known as UAV orthophotos, are high-resolution aerial images captured by drones equipped with cameras. These images undergo processing to correct distortions caused by terrain relief, camera tilt, and perspective, resulting in a uniform scale and accurate representation of the terrain Overall, drone orthophotos are valuable assets in the geospatial industry, providing accurate and detailed imagery for a wide range of applications, from disaster response and infrastructure inspection to environmental monitoring and precision agriculture. Their flexibility, high resolution, and quick deployment capabilities make them indispensable tools for visualizing, analyzing, and managing spatial data in various fields.
Standard Orthophotos
Standard orthophotos are aerial or satellite images that have undergone geometric correction to remove distortions caused by terrain relief, camera tilt, and other factors, but without the additional processing steps to eliminate all vertical relief displacement seen in true orthophotos. Overall, standard orthophotos are versatile and widely used in the geospatial industry, providing an accurate and reliable representation of the Earth's surface for a variety of mapping, analysis, and decision-making purposes. Their geometric accuracy, clarity, and compatibility with GIS software make them essential tools for visualizing and managing spatial data in a wide range of applications.
True Orthophotos
A true orthophoto is a specialized type of orthophoto that provides a highly accurate representation of the Earth's surface, with minimal distortion and relief displacement. Unlike standard orthophotos, which are created by projecting aerial or satellite imagery onto a digital elevation model (DEM) to correct for terrain relief, true orthophotos undergo additional processing to eliminate all vertical relief displacement, resulting in a completely planar representation of the terrain. Overall, true orthophotos offer a highly accurate and distortion-free representation of the Earth's surface, making them valuable tools for a wide range of applications requiring precise geospatial data and measurements. Their clarity, accuracy, and reliability make them indispensable in fields such as engineering, surveying, urban planning, agriculture, and natural resource management.
Natural color orthophotos
Natural color orthophotos are derived from aerial or satellite imagery captured using red, green, and blue (RGB) spectral bands. These orthophotos closely resemble how the human eye perceives the Earth's surface, with natural colors representing features such as vegetation, water bodies, buildings, and terrain. Overall, natural color orthophotos play a vital role in the geospatial industry by providing accurate and visually appealing representations of the Earth's surface. Their versatility, ease of interpretation, and compatibility with other GIS datasets make them valuable assets for a wide range of applications, from environmental monitoring to urban development.
False Color Orthophotos
False color orthophotos are derived from aerial or satellite imagery by assigning different spectral bands to the red, green, and blue color channels. Unlike natural color orthophotos, false color orthophotos use non-traditional combinations of spectral bands to highlight specific features or properties of the Earth's surface. Overall, false color orthophotos offer a powerful tool for extracting valuable information from aerial and satellite imagery. Their ability to enhance feature discrimination and highlight specific surface properties makes them invaluable for a wide range of applications in the geospatial industry, from natural resource management to environmental monitoring and agricultural productivity.
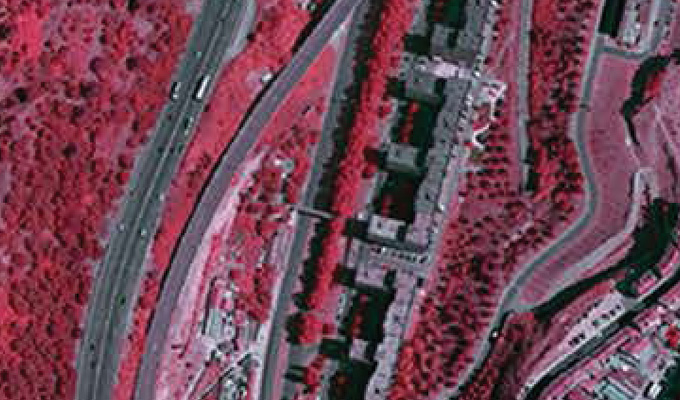
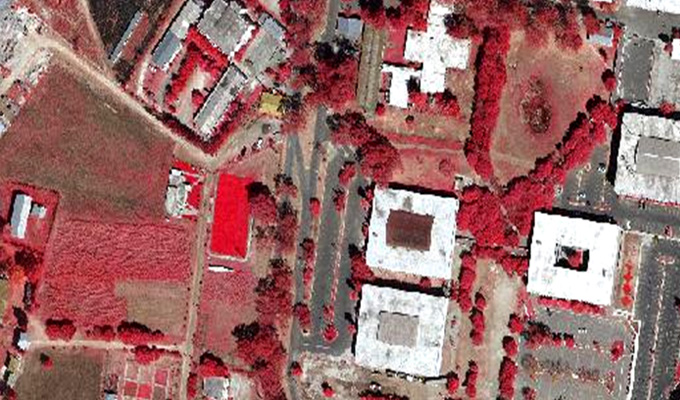
Infrared Orthophotos
Infrared (IR) orthophotos are derived from aerial or satellite imagery captured in the near-infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. These orthophotos provide valuable information about surface properties that may not be visible in visible light imagery. Overall, infrared orthophotos offer a powerful tool for analyzing surface properties and environmental conditions across a wide range of applications. Their ability to capture information beyond the visible spectrum makes them invaluable for vegetation assessment, land cover mapping, urban analysis, and environmental monitoring in the geospatial industry.
Multispectral Orthophotos
Multispectral orthophotos are created by combining imagery captured in multiple spectral bands beyond just red, green, and blue (RGB). These orthophotos provide valuable information about the Earth's surface by capturing variations in reflectance across different wavelengths of light. Overall, multispectral orthophotos offer a powerful tool for extracting valuable information from aerial and satellite imagery. Their ability to capture detailed spectral information across multiple bands enables a wide range of applications in vegetation analysis, land cover mapping, environmental monitoring, agriculture, and natural resource management in the geospatial industry.
In conclusion, orthophoto and mosaicing are essential tools in GIS that enable accurate mapping, visualization, and analysis of spatial data. Their high level of accuracy and ability to create detailed and seamless images make them invaluable for a wide range of applications in diverse fields. By leveraging the power of orthophotos and mosaics, GIS professionals can better understand and manage the complex spatial relationships that exist in our world.