Our Areas of Expertise
Delivering cutting-edge geospatial solutions across diverse industries

Forestry and Agriculture
Geospatial Solutions
Utilizing GIS for land use planning, crop management, forest management, and wildlife preservation to ensure sustainable practices.
Key Features:
- Land Use Planning: Mapping areas for various agriculture and forestry purposes.
- Crop Management: Monitoring crop distribution and health for efficient resource application.
- Forest Management: Mapping and monitoring forests for sustainable practices.
- Wildlife Management: Preserving and monitoring habitats for conservation efforts.
Telecommunications
Geospatial Solutions
Supporting the development and optimization of telecommunications networks using geospatial solutions.
Key Features:
- Planning of Telecommunications Networks: Identifying areas without internet connectivity and planning expansions.
- Site Selection for Towers: Analyzing suitability for telecommunications infrastructure.
- Network Optimization: Improving performance through spatial analytics.
- 5G Network Deployment: Supporting advanced network implementation.

Environment and Disaster Management
Geospatial Solutions
Applying geospatial technology to monitor environmental changes, assess risks, and coordinate disaster response.
Key Features:
- Environmental Monitoring: Using satellite imagery and aerial photography to track land use, vegetation, and water resources.
- Natural Resource Management: Mapping and monitoring resource distribution for sustainable conservation.
- Disaster Risk Assessment: Evaluating risks from natural disasters such as floods, landslides, and wildfires.
- Emergency Response: Coordinating rapid responses through geospatial data and analytics.

Transport, Logistics and Traffic Management
Geospatial Solutions
Leveraging geospatial technology for efficient transport planning, fleet management, and traffic management.
Key Features:
- Route Optimization: Optimizing routes by considering traffic patterns and road conditions.
- Fleet Management: Real-time tracking and monitoring of vehicle fleets.
- Asset Tracking: Managing assets like containers and cargo with GPS integration.
- Traffic Management: Implementing dynamic traffic control measures.
Property & Real Estate
Geospatial Solutions
Utilizing geospatial technology for property boundary mapping, real estate development, and infrastructure planning.
Key Features:
- Mapping of Property Boundaries: Monitoring changes in property ownership and planning for sustainable development.
- Management of Real Estate Development: Monitoring progress and sustainable planning.
- Valuation of Property: Analyzing market value for sale and purchase.
- Planning of Cities and Towns: Identifying development areas and planning infrastructure.

Natural Resources, Mining & Exploration
Geospatial Solutions
Leveraging geospatial technology for resource mapping, mining operations management, and sustainable exploration.
Key Features:
- Mapping of Natural Resources: Locating resources such as minerals, oil, and gas, monitoring extraction, and planning for sustainable use.
- Mining Operations Management: Managing mines, monitoring extraction, and planning for mine closure and rehabilitation.
- Geological Surveys: Conducting surveys for mineral resource identification and exploration activities.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Assessing and planning for sustainable resource extraction and mitigation strategies.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Monitoring and planning for the conservation of biodiversity hotspots.
- Water Resource Management: Managing water resources for sustainable use.
- Renewable Energy Development: Mapping and managing renewable energy resources and their environmental impacts.
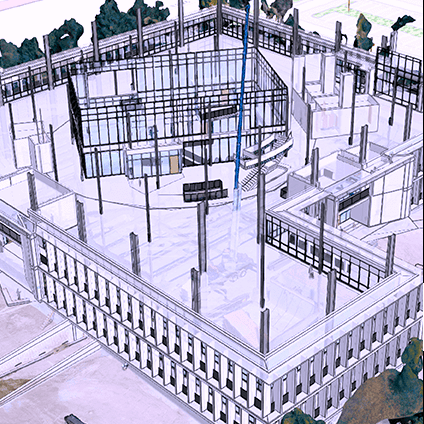

Architecture, Engineering & Construction
Geospatial Solutions
Utilizing geospatial solutions for site analysis, construction management, and infrastructure development.
Key Features:
- Site Analysis and Planning: Utilizing geospatial technologies for topography, geology, and environmental analysis.
- Construction and Surveying: Using GPS, LiDAR, and aerial photography for surveying and layout.
- Infrastructure Management: Managing and maintaining infrastructure through GIS data analysis.

Government
Geospatial Solutions
Utilizing geospatial technology for urban planning, emergency management, public health, infrastructure management, environmental management, land administration, and election administration.
Key Features:
- Urban Planning: Mapping cities and towns for development planning.
- Emergency Management: Using GIS for quick response to disasters and emergencies.
- Public Health: Tracking disease outbreaks and managing health resources.
- Infrastructure Management: Planning, monitoring, and maintaining roads, bridges, and water systems.
- Environmental Management: Monitoring air and water quality and supporting conservation efforts.
- Land Administration: Managing land use and registration of land titles.
- Elections Administration: Mapping electoral boundaries and managing election logistics.
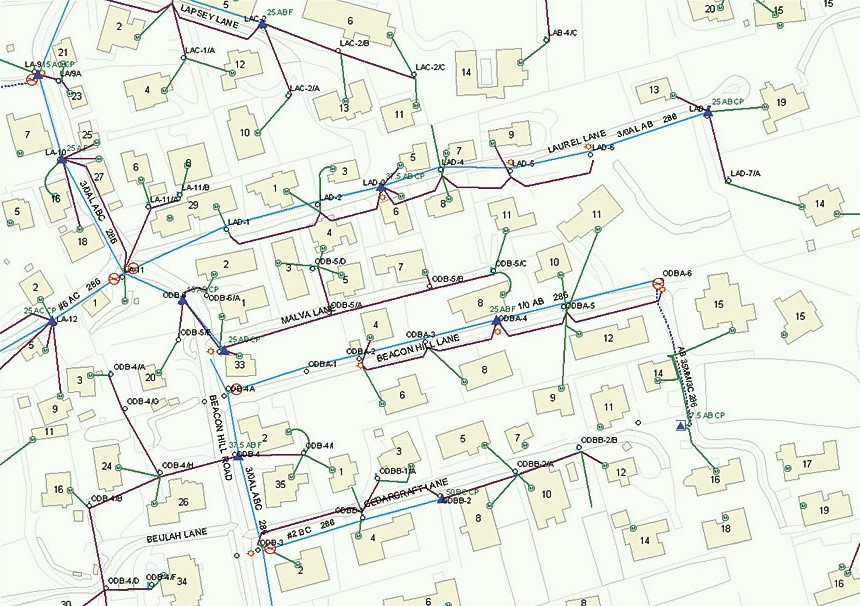
Energy & Utilities
Geospatial Solutions
Optimizing the siting, planning, and management of energy generation facilities and utility infrastructure using geospatial technology.
Key Features:
- Siting and Planning: Identifying optimal locations for energy generation facilities, such as wind farms, solar parks, and hydroelectric dams, based on factors like wind patterns, solar irradiation, and terrain.
- Infrastructure Management: Using GIS to store and analyze data about power lines, pipelines, and other utility assets for effective planning, maintenance, and repairs.
- Efficient Routing: Planning the most efficient routes for power lines and pipelines to minimize energy loss and reduce costs.
- Safety Enhancements: Leveraging geospatial data to improve safety in energy and utility operations by identifying and mitigating potential risks.