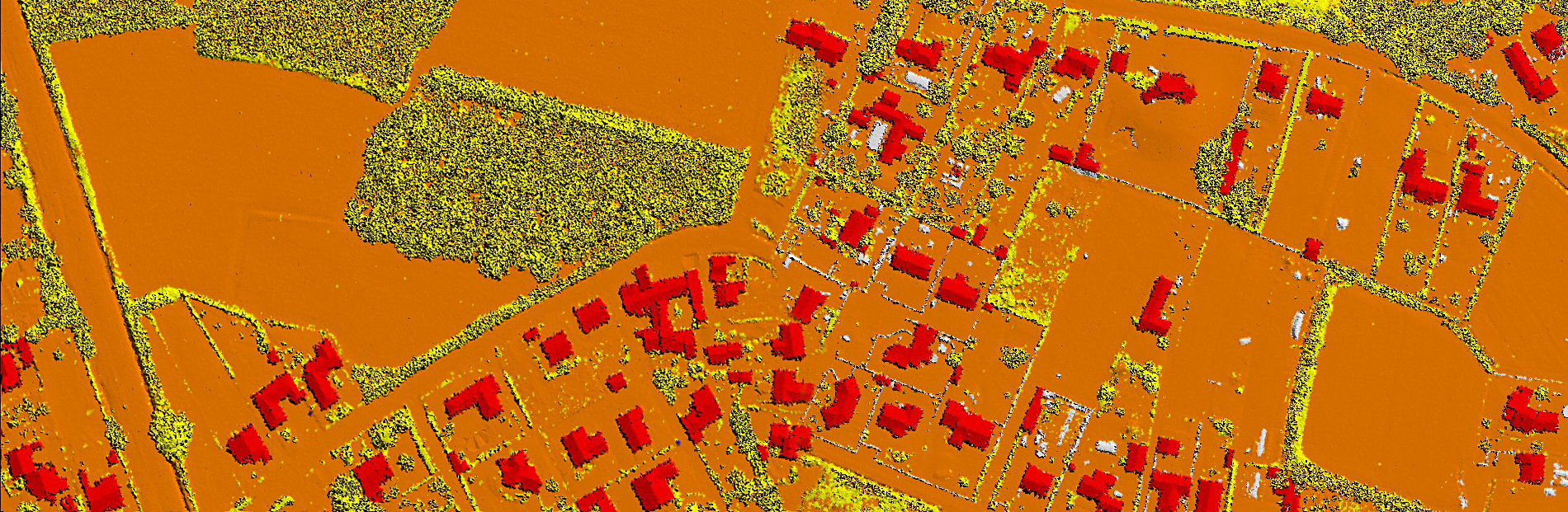
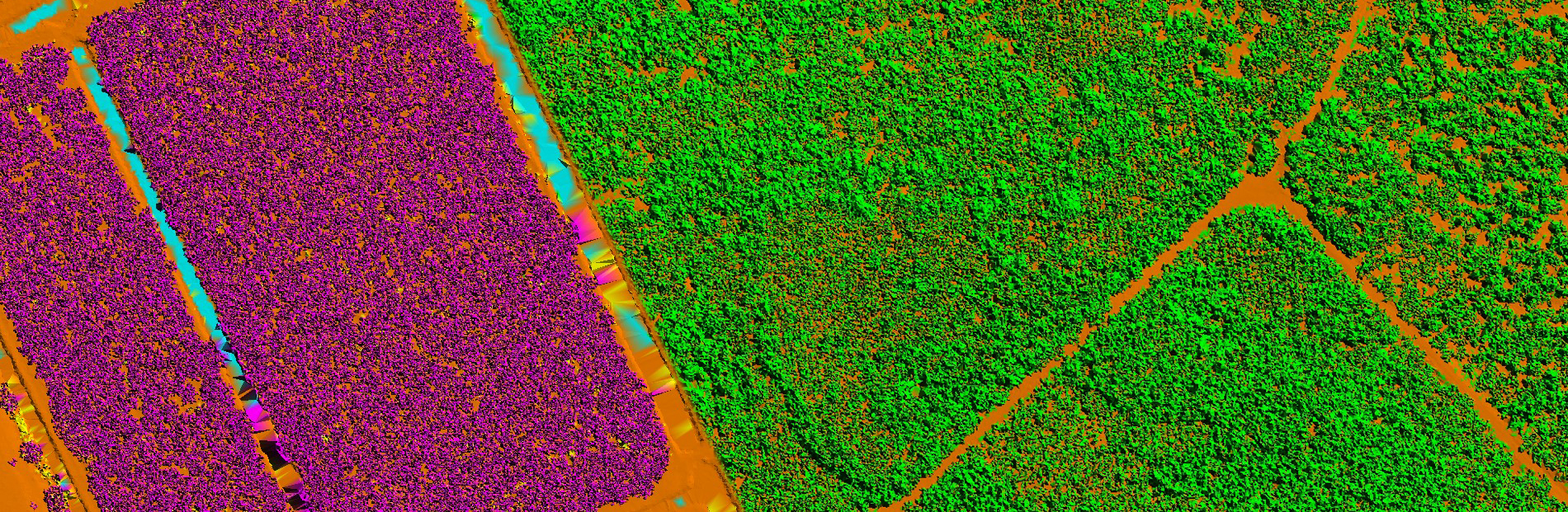
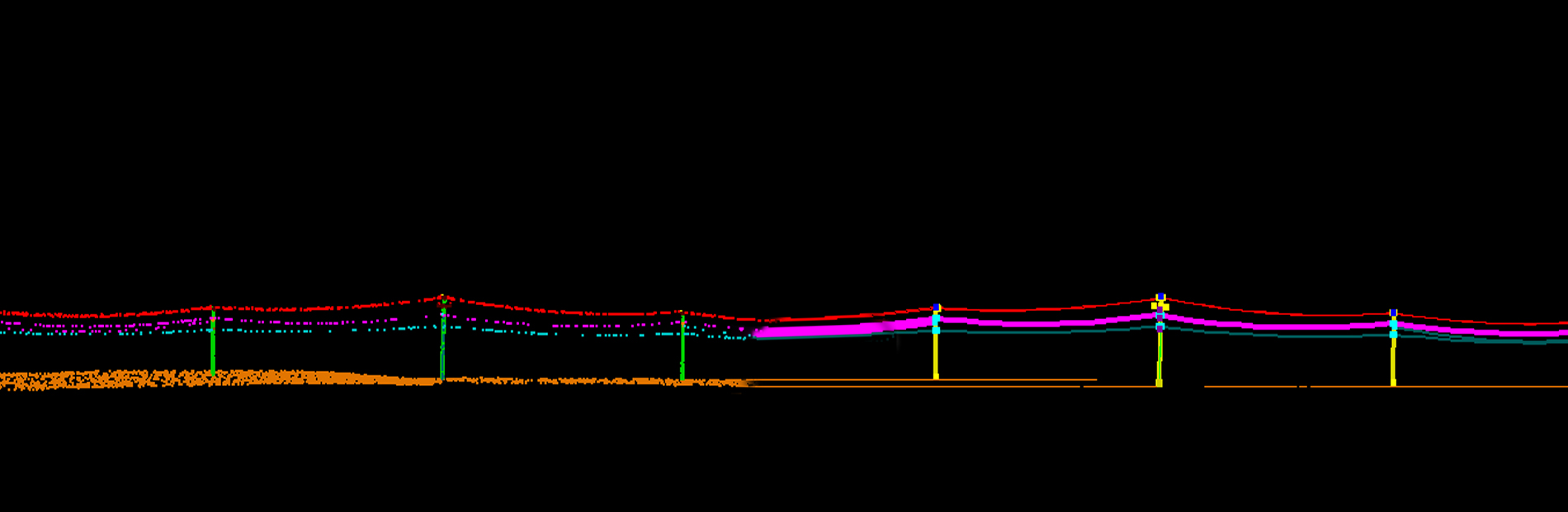
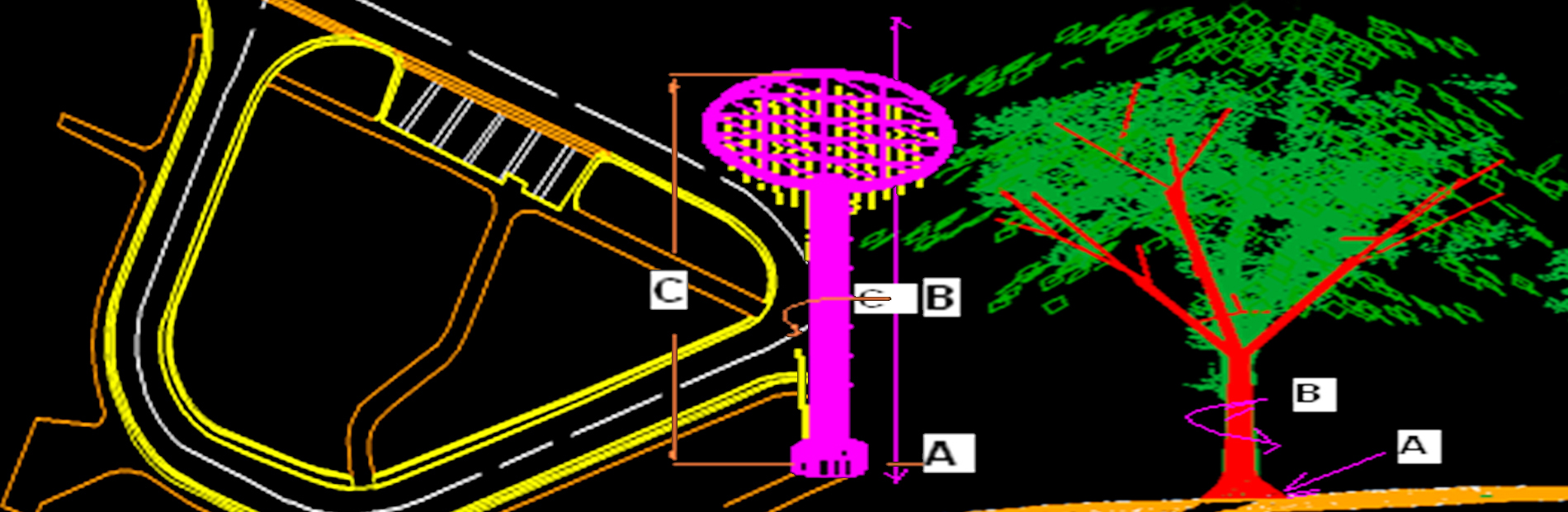
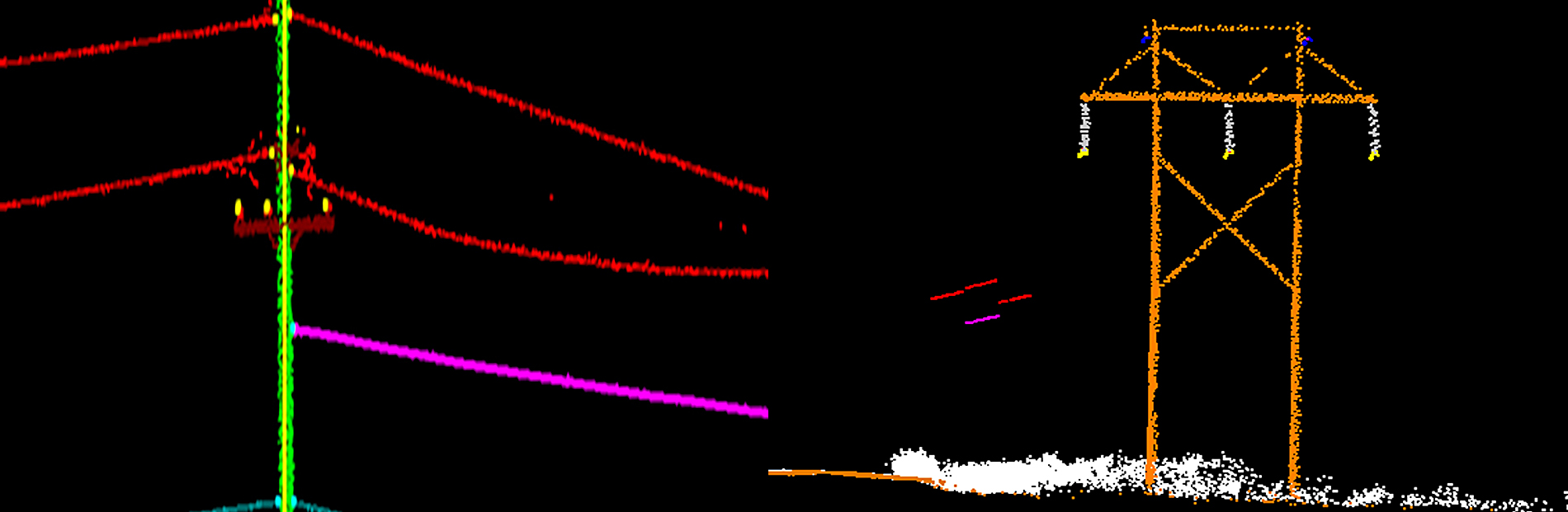

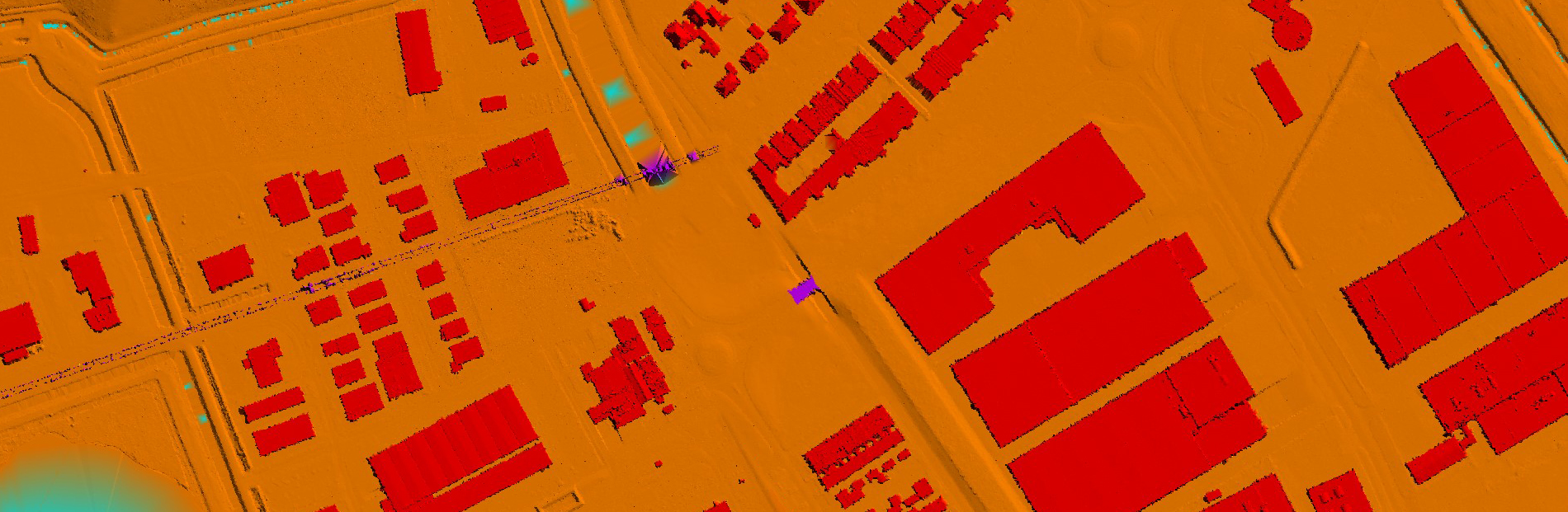
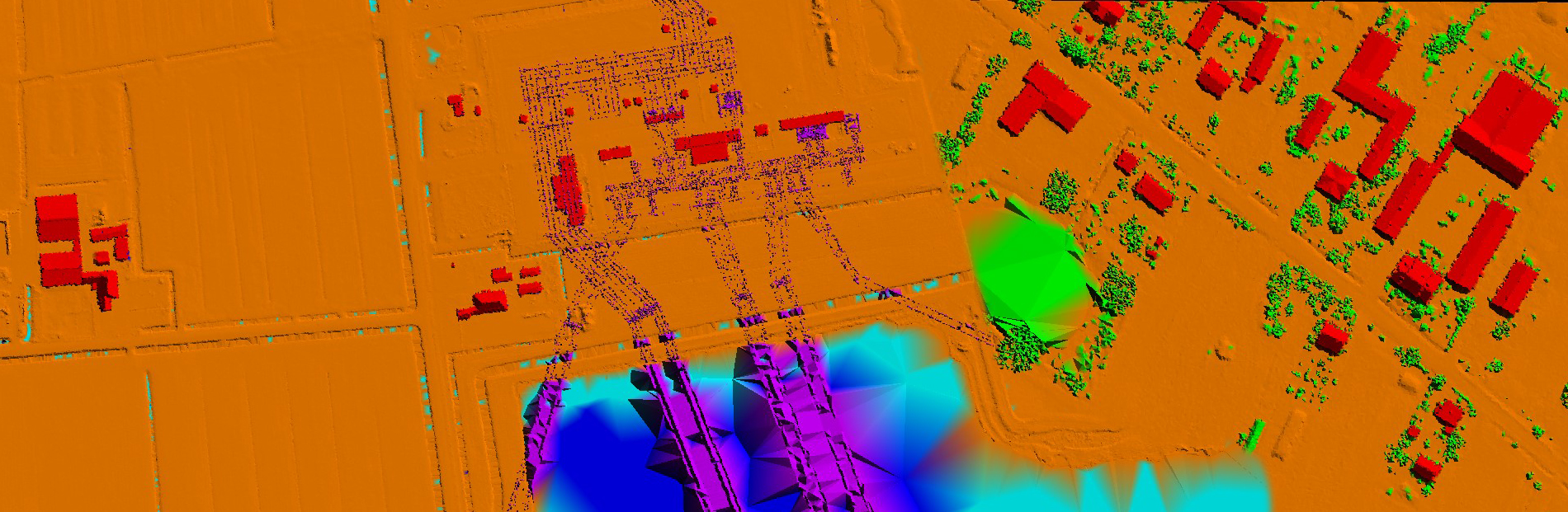
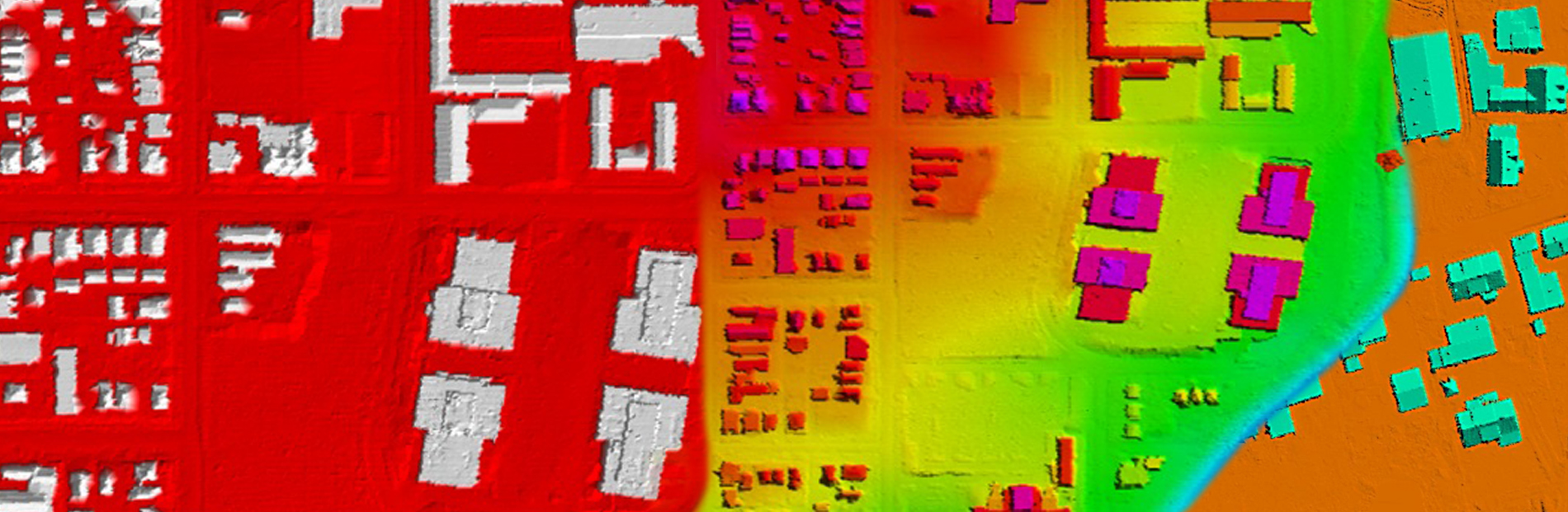
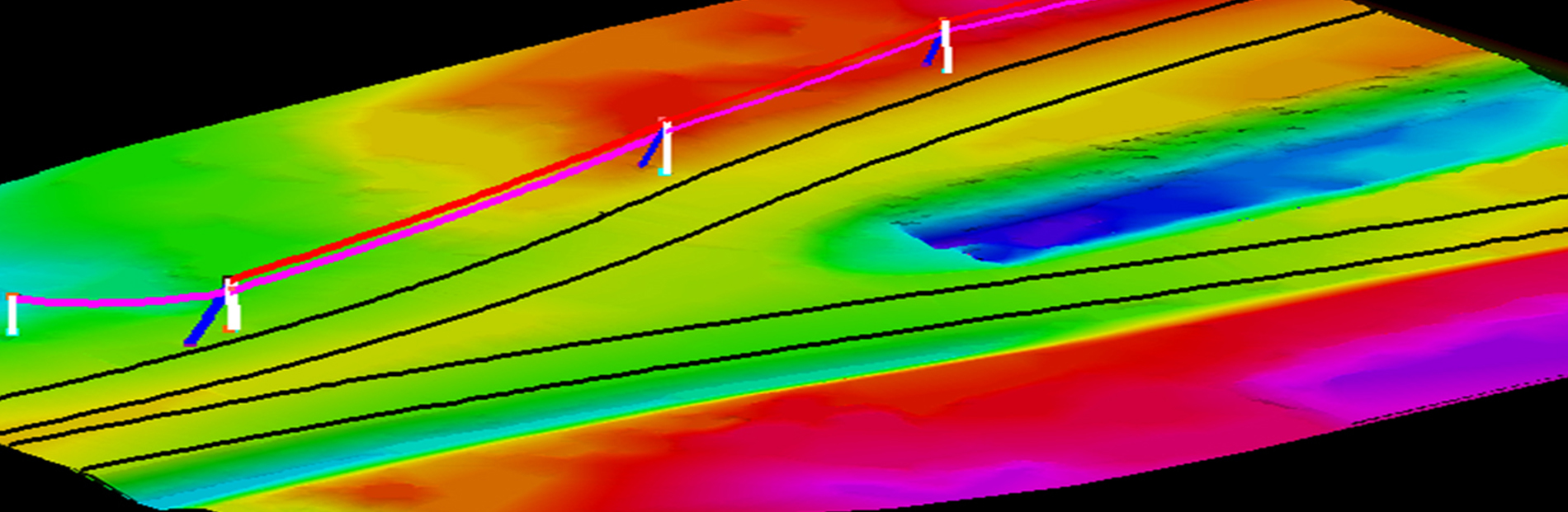

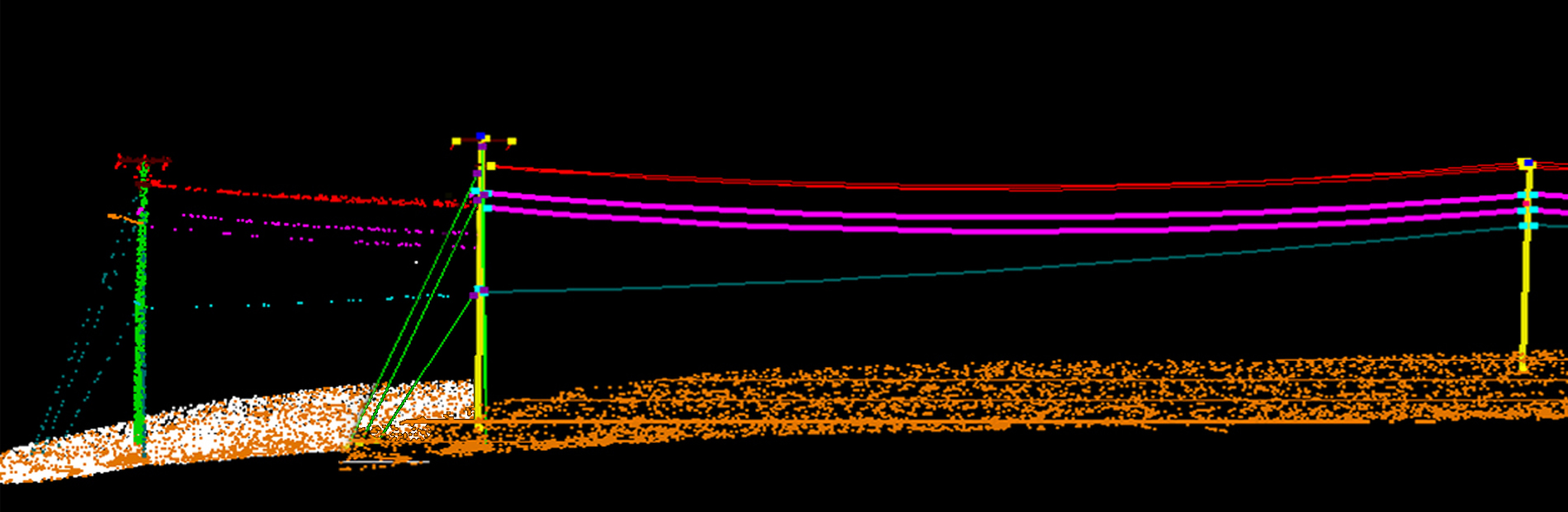


LiDAR Classification
AAMGST has a strong comprehensive hold on LiDAR processing of Airborne, Terrestrial, and Mobile data. LiDAR data has been classified and vectorized from various Scanners (Leica, RIEGL, and Optech) for different applications.
We have delivered one million hectares with high quality and reliable data to our Poland and US clients. We have technically exceptional and challenging LiDAR technicians to meet project deadlines. Our quality-driven LiDAR processing methodologies assure you high quality and fast turnaround.
Airborne LiDAR Classification
Airborne LiDAR is a remote sensing technique that uses laser pulses emitted from an aircraft to measure distances to the Earth's surface. It's one of the most widely used methods for collecting high-resolution elevation data and 3D information over large areas. Airborne LiDAR offers several advantages over other mapping techniques, including its ability to rapidly collect data over large areas, its high spatial resolution and accuracy, and its ability to penetrate vegetation and capture terrain features beneath tree canopies. These characteristics make airborne LiDAR a versatile and powerful tool for a wide range of geospatial applications.
Terrestrial LiDAR
Terrestrial LiDAR is a remote sensing technique that uses laser pulses emitted from a ground-based platform to measure distances to objects and terrain. It's commonly used for capturing detailed 3D information about small to medium-sized areas and objects with high precision and accuracy. Terrestrial LiDAR offers several advantages over other mapping techniques, including its ability to capture fine details and complex geometries with high precision, its flexibility for capturing data in diverse environments and conditions, and its suitability for applications requiring close-range measurements or indoor scanning. These characteristics make terrestrial LiDAR a versatile and powerful tool for a wide range of geospatial applications.
Mobile LiDAR
Mobile LiDAR is a remote sensing technique that uses laser pulses emitted from a moving platform, such as a vehicle or boat, to capture detailed 3D information about the surrounding environment. It's particularly useful for mapping transportation corridors, urban areas, and coastlines, where capturing data while in motion is advantageous. Mobile LiDAR offers several advantages over traditional LiDAR methods, including its ability to capture data quickly and efficiently over large areas, its suitability for capturing data in dynamic environments, and its ability to capture data from multiple perspectives simultaneously. These characteristics make mobile LiDAR a valuable tool for a wide range of geospatial applications.
UAV LiDAR
UAV LiDAR combines the benefits of LiDAR technology with the flexibility and accessibility of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), also known as drones. UAV LiDAR systems are increasingly popular for capturing highly accurate and detailed 3D information about terrain, infrastructure, and natural features UAV LiDAR offers several advantages over traditional LiDAR methods, including its ability to access hard-to-reach or hazardous areas, its flexibility for rapid deployment and data collection, and its cost-effectiveness for small-scale mapping projects. These characteristics make UAV LiDAR a valuable tool for a wide range of geospatial applications.
Spaceborne LiDAR
Spaceborne LiDAR refers to LiDAR technology deployed on satellites orbiting the Earth. Unlike airborne or terrestrial LiDAR, which operate from closer proximity to the Earth's surface, spaceborne LiDAR systems capture data from space, providing a unique perspective for mapping and monitoring purposes. Spaceborne LiDAR offers several advantages over traditional LiDAR methods, including its ability to capture data over large areas with global coverage, its suitability for mapping remote or inaccessible areas, and its ability to capture data consistently over time for long-term monitoring purposes. These characteristics make space borne LiDAR a valuable tool for a wide range of geospatial applications.
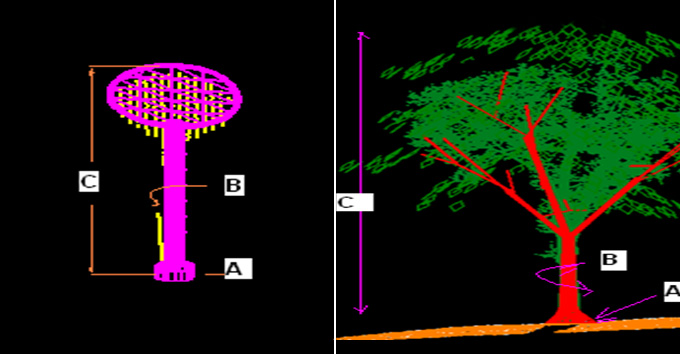
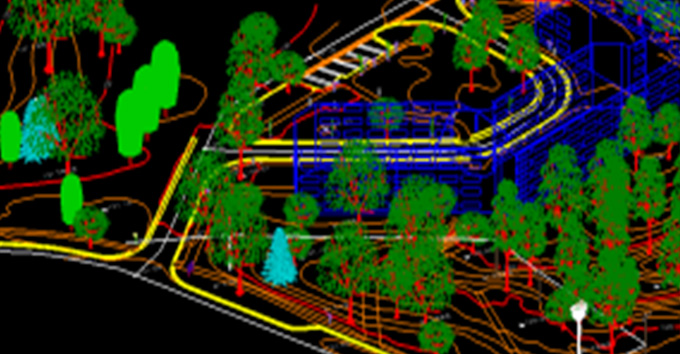
Another important aspect of LiDAR data processing is feature extraction, which involves identifying and extracting specific features from the LiDAR data. This includes extracting attributes such as tree heights, building heights, and road widths, which can be used for various applications such as flood risk assessment and urban infrastructure planning. LiDAR data can also be processed to create digital terrain models (DTMs) and digital surface models (DSMs), which provide detailed information about the elevation and morphology of the Earth's surface.
In addition to data classification and feature extraction, LiDAR data processing also involves data visualization and analysis. By visualizing LiDAR data in GIS software, analysts can gain a better understanding of the topography and features of a given area. Furthermore, by overlaying LiDAR data with other geospatial datasets such as satellite imagery and land cover data, analysts can perform advanced analyses and generate valuable insights for decision-making. Overall, LiDAR data processing in GIS is a powerful tool that enables the extraction of valuable information from LiDAR data, leading to informed decision-making and improved planning in various industries.