Aerial Triangulation
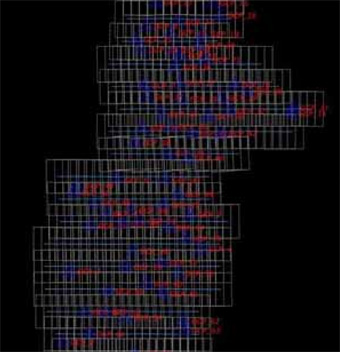
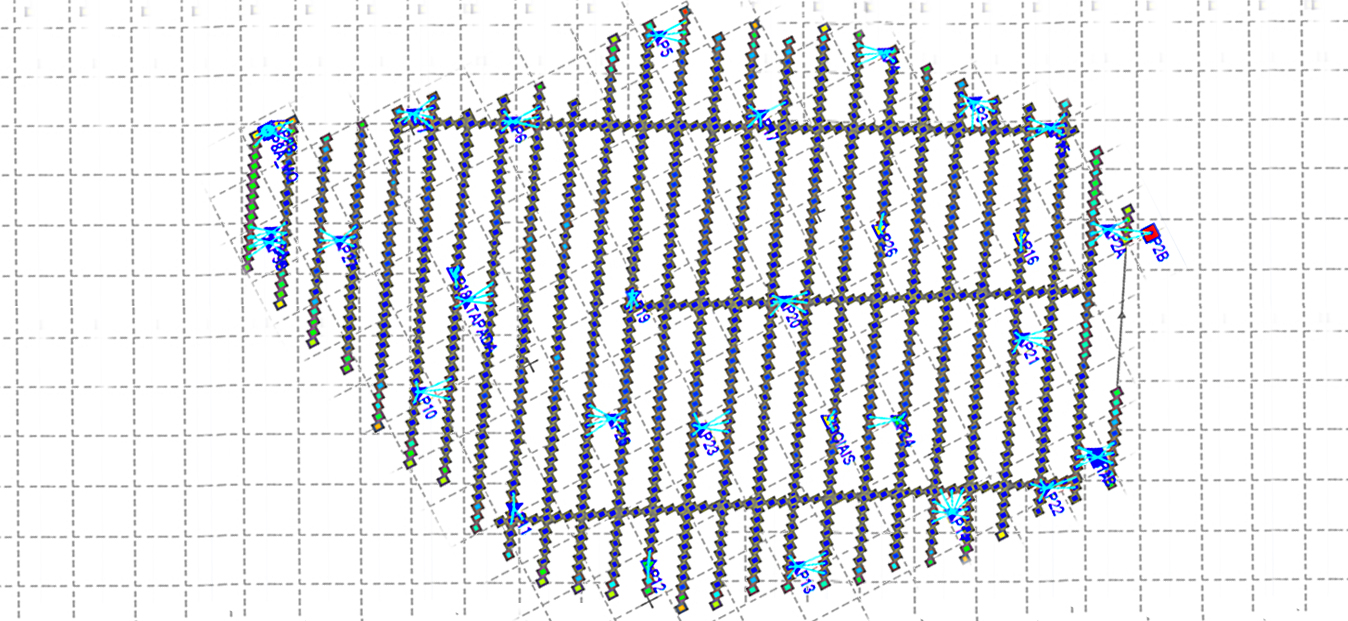
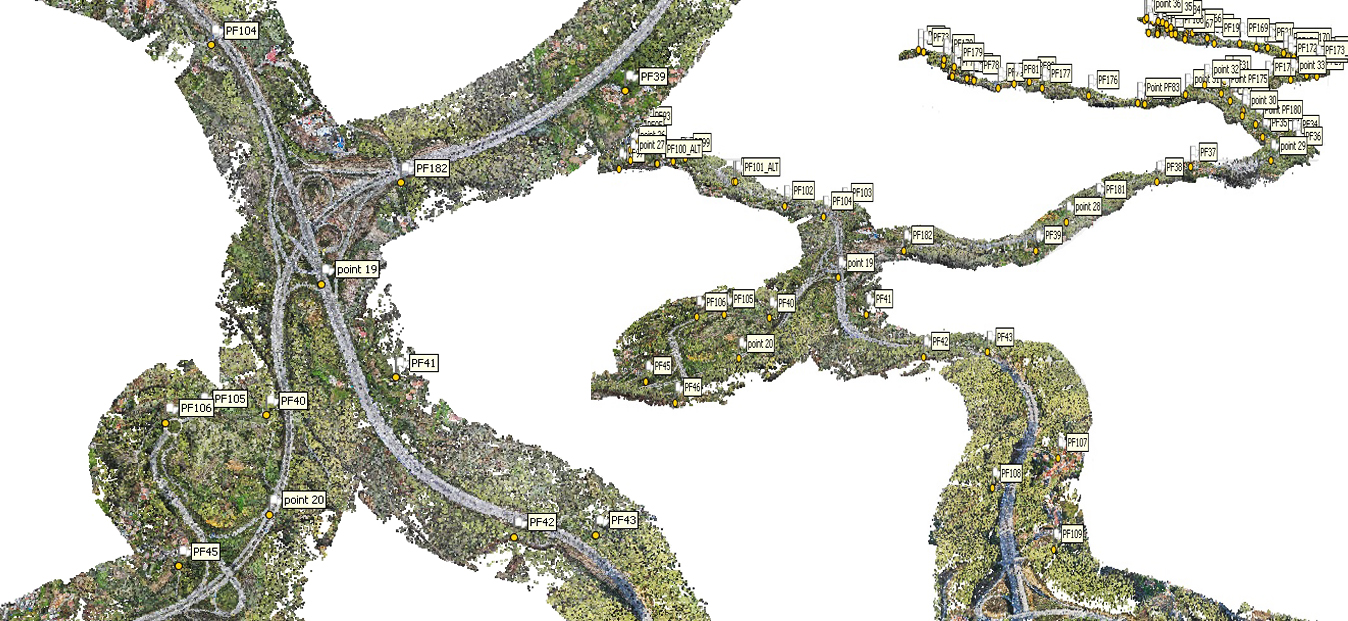
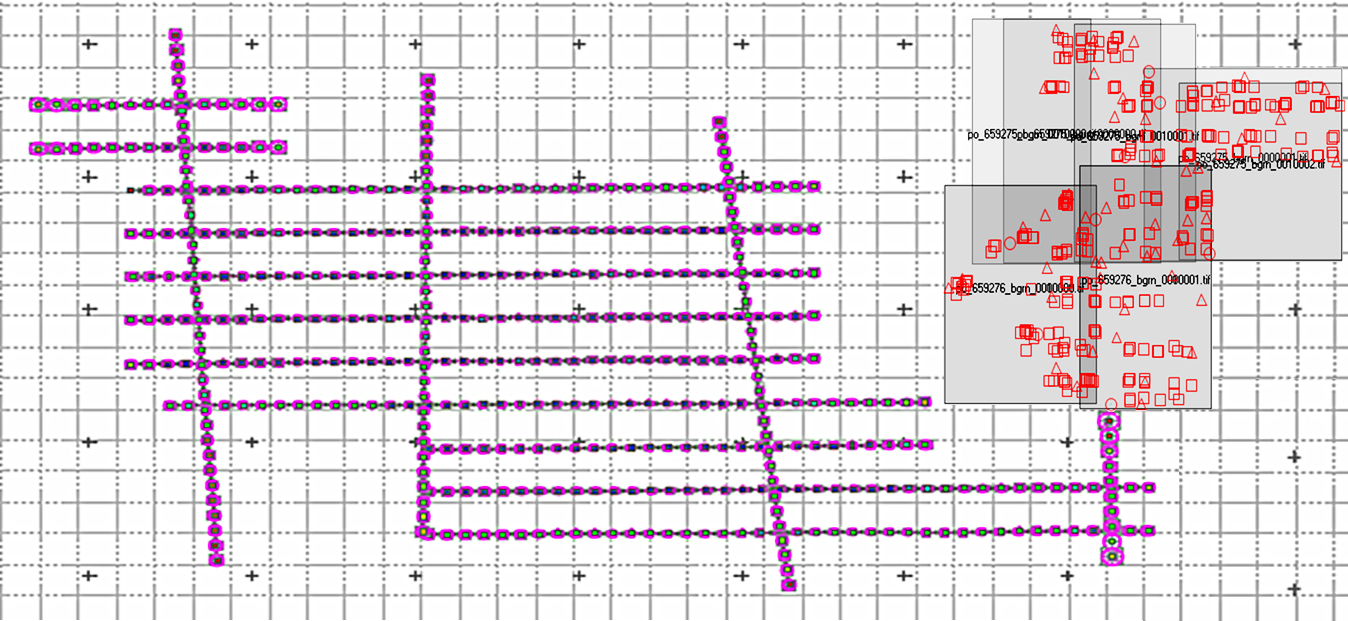
AAMGST is capable of doing Aerial Triangulation (AT) for both Aerial and Satellite imageries by using Automatic tie point extraction and manual measurement of Ground Control Points and additional tie points to produce accurate and reliable AT results. The AT results are presented in a standard document report file as per the client’s requirement to show the reliability of input data and accuracy statistics of the final results.
Aerial triangulation is a crucial process in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) that involves using overlapping aerial photographs to accurately determine the position of points on the Earth’s surface. This technique is essential for creating accurate maps and models of terrain and infrastructure. Aerial triangulation involves identifying common points on multiple aerial photographs and using geometric principles to calculate the exact three-dimensional coordinates of these points. This process helps ensure that GIS data is precise and reliable for various applications, such as urban planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster management.
One of the main advantages of Aerial Triangulation in GIS is its ability to produce high-quality and detailed maps. By accurately determining the position of points on the ground, aerial triangulation allows for the creation of highly accurate maps that can be used for a variety of purposes, such as land surveying, transportation planning, and natural resource management. This level of precision is essential for decision-making and analysis in various fields, as accurate spatial data is key to understanding the relationships between different geographical features and phenomena.
Aerial Triangulation also plays a crucial role in the creation of digital elevation models (DEMs) and three-dimensional models of the Earth’s surface. By accurately determining the position of points on overlapping aerial photographs, GIS professionals can generate detailed topographic maps that represent the terrain with high precision. These models are essential for various applications, such as flood risk assessment, site suitability analysis, and infrastructure design. Aerial triangulation helps ensure that these models are accurate and reliable, providing valuable insights for planning and decision-making.
Overall, Aerial Triangulation is a fundamental process in GIS that is essential for producing accurate and reliable spatial data. By accurately determining the position of points on the Earth’s surface, this technique enables the creation of high-quality maps, models, and analyses that support a wide range of applications. As technology continues to advance, aerial triangulation techniques are becoming more sophisticated and efficient, allowing GIS professionals to generate increasingly detailed and accurate spatial data for a variety of purposes.
Satellite Aerial Triangulation
The term "satellite aerial triangulation" is a bit of a misnomer because aerial triangulation traditionally refers to the process of triangulating ground points from overlapping aerial photographs captured by aircraft. However, satellite imagery can also be used in a similar process, but it's typically referred to as satellite image triangulation or simply image triangulation. In this context, satellite image triangulation involves establishing accurate ground positions of points visible in overlapping satellite images by measuring the angles between them from multiple satellite perspectives. This process is similar in principle to aerial triangulation but is applied to satellite imagery captured by remote sensing satellites orbiting the Earth. Satellite image triangulation is commonly used in remote sensing applications for mapping, land surveying, environmental monitoring, and other geospatial tasks. It enables the generation of orthorectified satellite images, digital elevation models (DEMs), and other geospatial products that are essential for various applications in the geospatial industry.
Drone Triangulation
Drone triangulation, also known as UAV triangulation or aerial triangulation using drone imagery, refers to the process of establishing accurate ground positions of points visible in overlapping images captured by drones equipped with cameras. This process is similar to traditional aerial triangulation but is adapted to the characteristics and capabilities of drone-based imagery. Drone triangulation is commonly used in various applications, including mapping, surveying, 3D modeling, construction site monitoring, agriculture, environmental assessment, and infrastructure inspection. It offers advantages such as flexibility, rapid data acquisition, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility, making it an increasingly popular choice for geospatial data collection and analysis.
Direct Georeferencing
Direct georeferencing is a technique used in photogrammetry and remote sensing to determine the precise position and orientation of an imaging sensor (such as a camera) directly from onboard navigation and positioning sensors, without the need for ground control points (GCPs). This method relies on integrating Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers, Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs), and optionally other sensors to provide accurate positioning, attitude (orientation), and velocity information for the imaging platform. Direct georeferencing is commonly used in UAV (drone) mapping, aerial photogrammetry, mobile mapping systems, airborne LiDAR, and other applications where accurate and efficient georeferencing of sensor data is required.